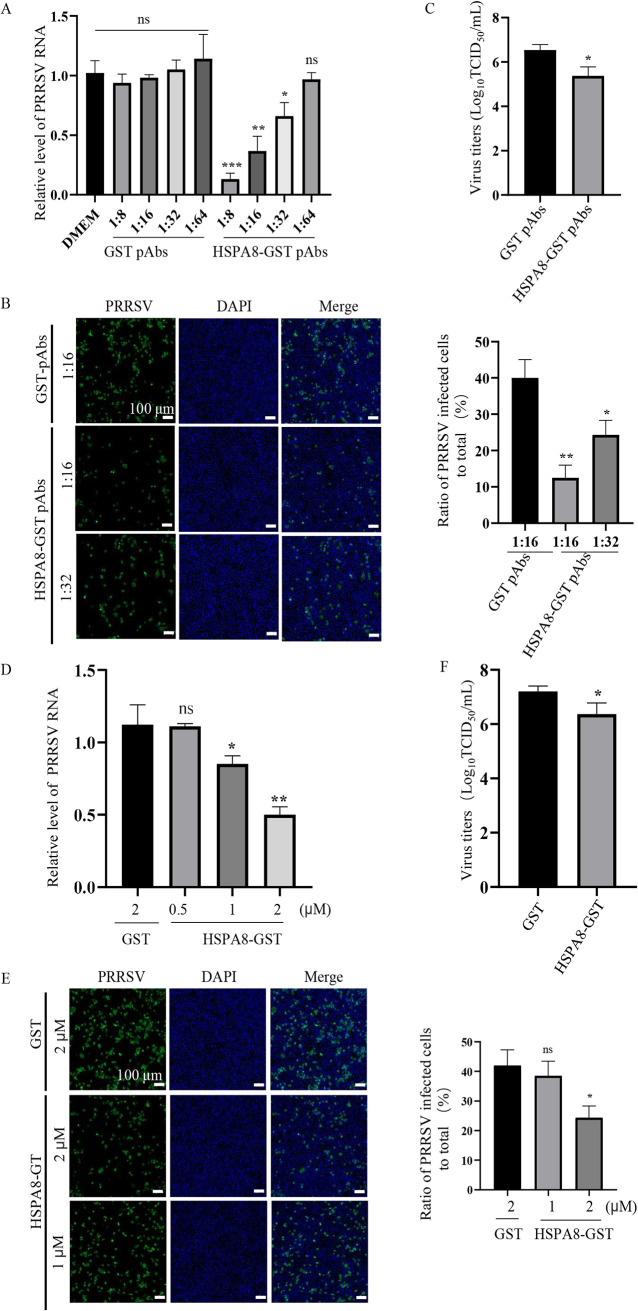
FIG 5.
HSPA8 pAbs and soluble HSPA8 protein inhibit PRRSV infection in MARC-145 cells. (A, C) HSPA8 pAbs inhibited PRRSV infection. MARC-145 cells were incubated with different folds of diluted HSPA8-GST pAbs or GST pAbs at 37°C for 1 h. Then the cells were washed with PBS and incubated with PRRSV (0.1 MOI) at 4°C for 1 h. After three washes, the cells were again incubated with the corresponding pAbs in DMEM at 37°C for 24 h. PRRSV RNA abundance was determined by RT-qPCR (A). PRRSV infectivity was detected by IFA, and the ratio of PRRSV-infected cells to total was calculated. Scale bars, 100 μm (B). Viral titers were determined by detecting TCID50 (C). Data represent means ± SD from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, no significant difference. (D, E) Soluble HSPA8 protein inhibited PRRSV infection. PRRSV at 0.1 MOI was incubated with HSPA8-GST (0.5, 1, 2 μM) or GST protein (2 μM) at 37°C for 1 h and then inoculated in MARC-145 cells for 1 h. The cells were washed with PBS and then harvested at 24 h. PRRSV RNA abundance was determined by RT-qPCR (D). PRRSV infectivity was detected by IFA, and the ratio of PRRSV-infected cells to total was calculated. Scale bars, 100 μm (E). Viral titers were determined by detecting TCID50 (F). Data represent means ± SD from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference.