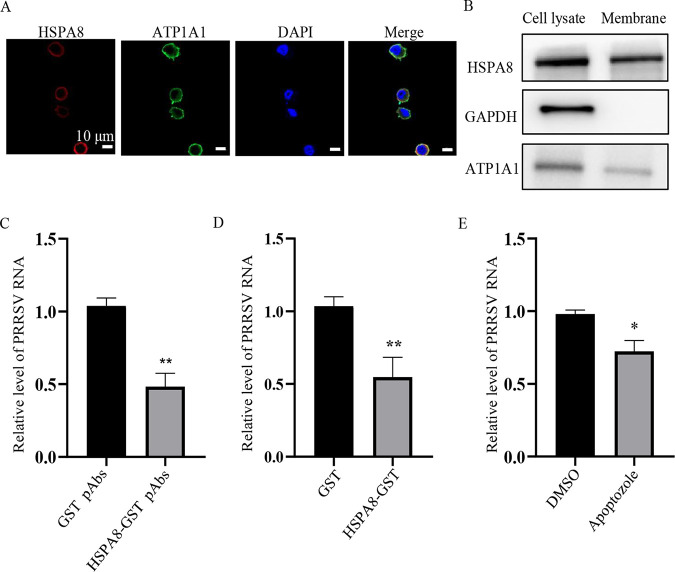
FIG 7.
HSPA8 is important for PRRSV attachment and internalization in CRL-2843-CD163 cells. (A, B) HSPA8 was expressed both on the cell surface and in the cytoplasm of CRL-2843-CD163 cells. CRL-2843-CD163 cells were fixed with 4% PFA, stained with anti-HSPA8 MAb (catalog no. 66442-1-AP; red) and anti-ATP1A1 pAbs (green), respectively. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue) by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm (A). WCLs and membrane extracts of CRL-2843-CD163 were subjected to IB using anti-HSPA8 pAbs (catalog no. 10654-1-AP), anti-ATP1A1 pAbs and anti-GAPDH MAb (B). (C) HSPA8 pAbs inhibited PRRSV infection. CRL-2843-CD163 cells were incubated with HSPA8-GST pAbs and GST pAbs at 1:16 dilution in DMEM at 37°C for 1 h. Then the cells were washed with PBS and inoculated with PRRSV (0.3 MOI) at 4°C for 1 h. After three washes, the cells were again incubated with DMEM containing the corresponding antibodies for 24 h. PRRSV RNA abundance was determined by RT-qPCR. Data represent means ± SD from three independent experiments. **, P < 0.01. (D) Soluble HSPA8 protein inhibited PRRSV infection. PRRSV at 0.3 MOI was incubated with HSPA8-GST or GST protein at the final concentration of 2 μM at 37°C for 1 h, and then inoculated in CRL-2843-CD163 cells and harvested at 24 h. PRRSV RNA abundance was determined by RT-qPCR. Data represent means ± SD from three independent experiments. **, P < 0.01. (E) HSPA8 inhibitor suppressed PRRSV infection. CRL-2843-CD163 cells were treated with apoptozole (25 μM) and infected with PRRSV at 0.3 MOI for 1 h. After three washes, the cells were again cultured for 24 h. PRRSV RNA abundance were determined by RT-qPCR. Data represent means ± SD from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05.