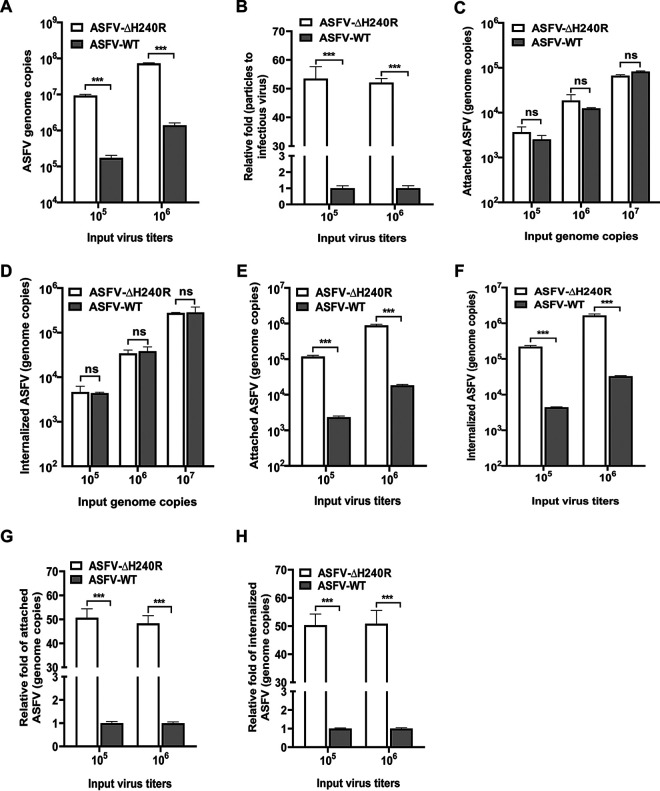
FIG 7.
The H240R protein is not required for ASFV binding to or entry into PAMs. (A) Genome copies of ASFV-ΔH240R or ASFV HLJ/2018 (ASFV-WT) per 105 and 106 HAD50. Genome copies were determined from 105 and 106 HAD50 ASFV-ΔH240R or ASFV-WT by quantitative PCR (qPCR) based on B646L. (B) ASFV-ΔH240R or ASFV-WT particle-to-infectious virus ratios. The particle-to-infectious virus ratios of ASFV-ΔH240R are nearly 50 times higher than those of ASFV-WT based on samples from panel A. (C and E) The attachment levels of ASFV-ΔH240R or ASFV-WT were similar. Equal numbers of genome copies (105, 106, and 107) (C) or equal titers (105 and 106) (E) of ASFV-ΔH240R or ASFV-WT were added to PAMs at 4°C and allowed to attach for 1 h. The numbers of genome copies of attached ASFVs were quantified by qPCR. (G) The fold change in attached ASFV-ΔH240R was nearly 50 times higher than that of ASFV-WT with equal titers (E). (D and F) The internalization levels of ASFV-ΔH240R and ASFV-WT were similar. Equal numbers of genome copies (105, 106, and 107) (D) or equal titers (105 and 106) (F) of ASFV-ΔH240R or ASFV-WT were added to PAMs at 37°C and allowed to internalize for 2 h. The genome copies of internalized ASFVs were quantified by qPCR. (H) The fold change in internalized ASFV-ΔH240R was approximately 50 times higher than that of ASFV-WT with equal titers (F). The data shown are from three independent experiments. Error bars denote standard errors of the means. The significance of differences between groups (n = 3) was determined using Student's t test (***, P < 0.001). ns, not significant.