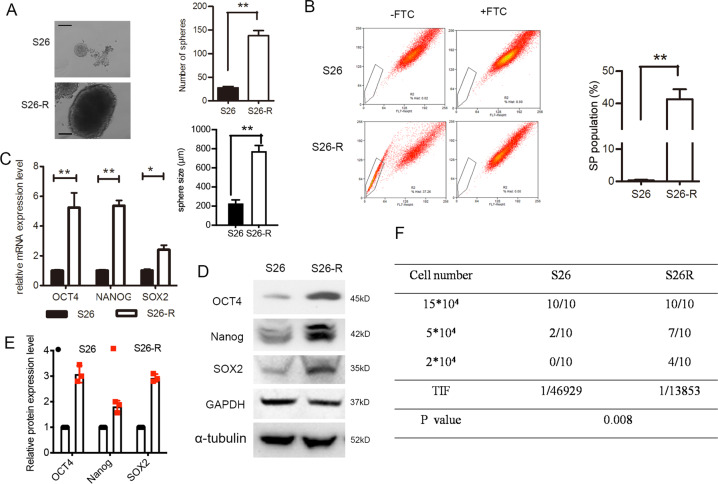
Fig. 2. Ionizing radiation enhanced CSC subpopulation enrichment and radioresistance in vitro and in vivo.
A Single-cell suspensions were seeded in ultra-low-attachment culture plates. The formed spheroids were counted via microscopy. Representative images are shown, the number (upper) and the size (lower) of S26 and S26-R cells were compared, **p < 0.01, Student’s t-test, Scale bar: 200 μm. B Percentages of SP cells are shown in the left panel; three independent experiments were performed; The right panels show the upregulation of SP in cells S26-R NPC cells, **p < 0.01, Student’s t-test. C (Left) mRNA levels of stem-cell markers were determined by quantitative PCR analysis, ACTB (encoding β-actin) was used as a control. (Right) protein levels of stem-cell markers as determined using western blotting; β-actin was used as the loading control. D A total of 2 × 104, 5 × 104, and 15 × 104 of S26 and its radio-resistant S26-R NPC cells were subcutaneously injected into NOD/SCID mice (n = 10 mice/group). A summary of tumorigenicity in mice is shown. The TIF and p-value were calculated by using ELDA software. (NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma; CSC, cancer stem cell; SP, side population; NOD, non-obese diabetic; SCID, severe combined immunodeficiency; TIF, tumor-initiating cell frequency; ELDA, extreme limiting dilution analysis).