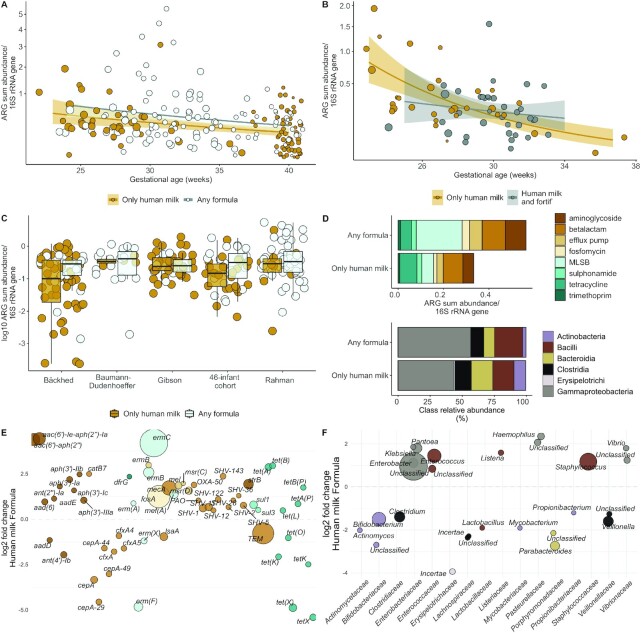
FIGURE 4.
Effect of formula feeding on neonatal gut resistome in meta-analysis cohorts. (A) Differences in relative ARG sum abundance/16S rRNA gene copy numbers in infants only fed human milk or any formula. (n = 206; n = 180 for other cohorts; n = 26 for infants not fed fortifier in the train set cohort). Formula feeding was associated with an approximately 70% increase in the relative abundance of ARGs in the meta-analysis [n = 180; gamma-distributed GLM, fold change 1.69 (95% CI 1.12, 2.55); P = 0.013, adjusting for gestational age and 16S rRNA counts]. (B) Differences in relative ARG sum abundance/16S rRNA gene copy numbers in infants fed human milk or any fortifier (n = 67). Neither supplementation of the infant's own mother's milk with fortifier or donor milk had a significant effect on the ARG load (gamma-distributed GLM, P = 0.42 for fortifier; P = 0.91 for donor milk, adjusting for 16S rRNA counts and gestational age). (A and B) A regression line is fitted using gamma-distributed GLMs. The y axes have been square root transformed. Dot sizes depict infant ages, with larger dots being older infants. (C) Effect of formula on ARG load in meta-analysis data sets by cohort (n = 206). The boxplot hinges represent 25% and 75% percentiles and centerline the median. Notches are calculated with the formula median ± 1.58 × IQR/sqrt (n). (D) Differences between most abundant ARG and bacterial classes by diet in meta-analysis data sets. (E) Differentially abundant ARGs in infants with different diets using DESeq2 analysis and an adjusted P value cutoff of 0.05 for reported genes. Genes with positive values are more abundant in formula-fed infants, and genes with negative values are more abundant in exclusively human milk–fed infants. (F) Differentially abundant genera in infants with different diets using DESeq2 analysis and an adjusted P value cutoff of 0.05 for reported genera. Genes and genera with positive values are more abundant in formula-fed infants, and genes with negative values are more abundant in exclusively human milk–fed infants. (E and F) The larger the point size, the more abundant the gene is in the samples. Abbreviations: ARG, antibiotic resistance gene; GLM, generalized linear mode; MLSB, macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B; rRNA, ribosomal RNA.