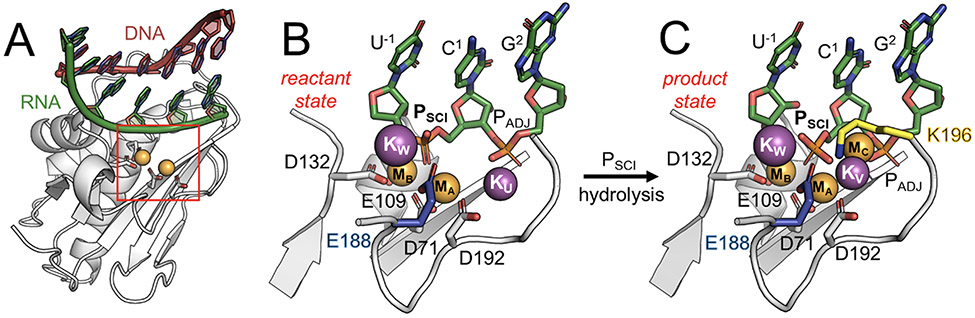
Figure 1.
RNase H1 catalytic intermediates captured by time-resolved X-ray crystallography.35 (A) Overview of the RNase H1 (white) in complex with an RNA:DNA hybrid (green:red). (B) Catalytic site before RNA hydrolysis (i.e., reactant state, PDBid: 6DO9). The catalytic residues forming the DEDD motif (D71, E109, D132 and D192; white) and the second shell residue E188 (blue) are represented as sticks. RNA nucleotides (green) including the scissile phosphate (PSCI) and its adjacent phosphate (PADJ) are also shown. The two catalytic magnesium ions MA-MB (orange) and the additional potassium ions KW and KU (purple) are shown as spheres. (C) Catalytic site upon RNA hydrolysis (i.e., product state, PDBid: 6DOX). Here, KU is replaced by the third divalent metal ion MC (orange), or by the monovalent KV (purple), while the second-shell residue K196 (yellow) can directly interact with the scissile phosphate.