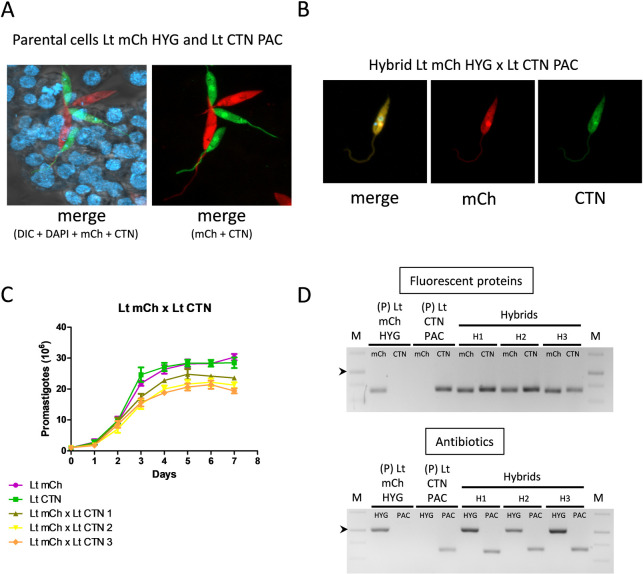
Fig 2. Characterization of intraclonal hybrids.
(A) Confocal microscopy showing the interaction between LULO cells and parental cell lines of L. tropica before mating. (B) Representative image of confocal microscopy of one hybrid clon of L. tropica mCh HYG x L. tropica CTN PAC and fluorescence emission in the mCh (561 nm) and CTN (488 nm) channels. (C) Growth curves (number of promastigotes in culture during 7 days) of the parental L. tropica mCh HYG (Lt mCh) and L. tropica CTN PAC (Lt CTN), and three representative intraclonal hybrids (Lt mCh x Lt CTN 1, 2 and 3). (D) Agarose gels of the electrophoresis of the PCR products obtained after the amplification of the genes encoding fluorescent proteins (mCh and CTN) and antibiotic resistance (HYG or PAC) in the parental (P) and three representative intraclonal hybrids (H). The arrowheads indicate the 1000 bp band in the DNA molecular weight marker (M).