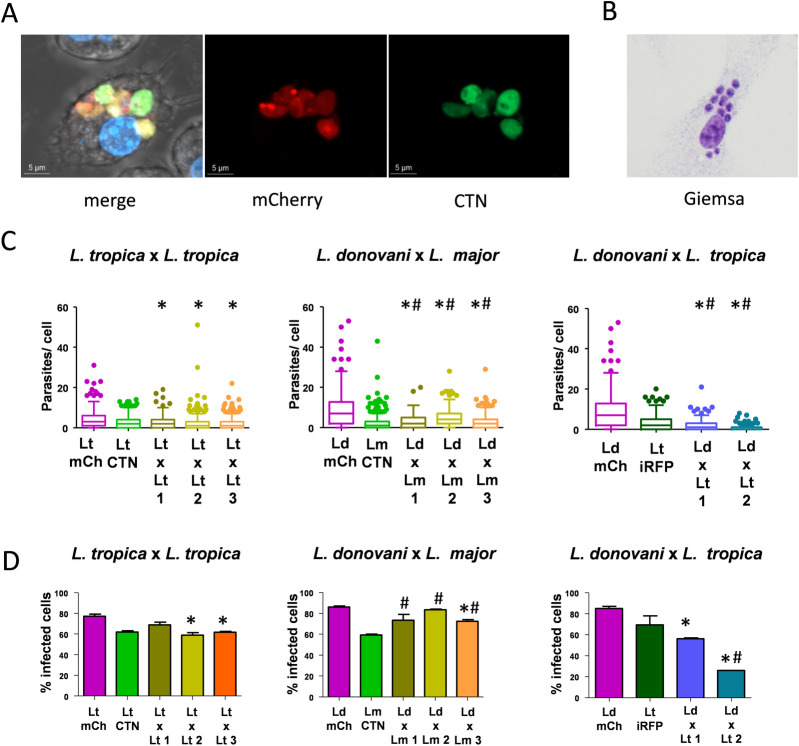
Fig 8. Infectivity of intraclonal and interspecies hybrids.
(A) Representative image of confocal microscopy of a RAW cell infected with one hybrid of L. donovani mCh HYG x L. major CTN PAC. Merge and fluorescent pictures in the mCh (561 nm) and CTN (488 nm) channels are shown. (B) Representative image of BMMs infected with amastigotes of one hybrid of L. donovani mCh HYG x L. major CTN PAC and stained with Giemsa. (C) Box plots representing the number of amastigotes present within each BMM after in vitro infection withamastigotes of L. tropica mCh HYG (Lt mCh), L. tropica CTN PAC (Lt CTN), three intraclonal hybrids L. tropica mCh HYG x L. tropica CTN PAC (Lt x Lt 1, 2 and 3), L. donovani mCh HYG (Ld mCh), L. major CTN PAC (Lm CTN) three interspecies hybrids L. donovani mCh HYG x L. major CTN PAC (Ld x Lm 1, 2 and 3), L. tropica iRFP PAC (Lt iRFP), and two interspecies hybrids L. donovani mCh HYG x L. tropica iRFP PAC (Ld x Lt 1 and 2). (D) Bar graphs representing the percentage of infected BMMs after in vitro infection withamastigotes of L. tropica mCh HYG (Lt mCh), L. tropica CTN PAC (Lt CTN), three intraclonal hybrids L. tropica mCh HYG x L. tropica CTN PAC (Lt x Lt 1, 2 and 3), L. donovani mCh HYG (Ld mCh), L. major CTN PAC (Lm CTN) three interspecies hybrids L. donovani mCh HYG x L. major CTN PAC (Ld x Lm 1, 2 and 3), L. tropica iRFP PAC (Lt iRFP), and two interspecies hybrids L. donovani mCh HYG x L. tropica iRFP PAC (Ld x Lt 1 and 2). Differences were considered as significant when p<0,05 and in a Kruskal-Wallist test (C) or in a one-way ANOVA analysis (D) (represented with an asterisk regarding the first parental line and with a hash regarding the second parental line).