Figure 1. Mechanisms of somatic mutations giving rise to tissue mosaicism.
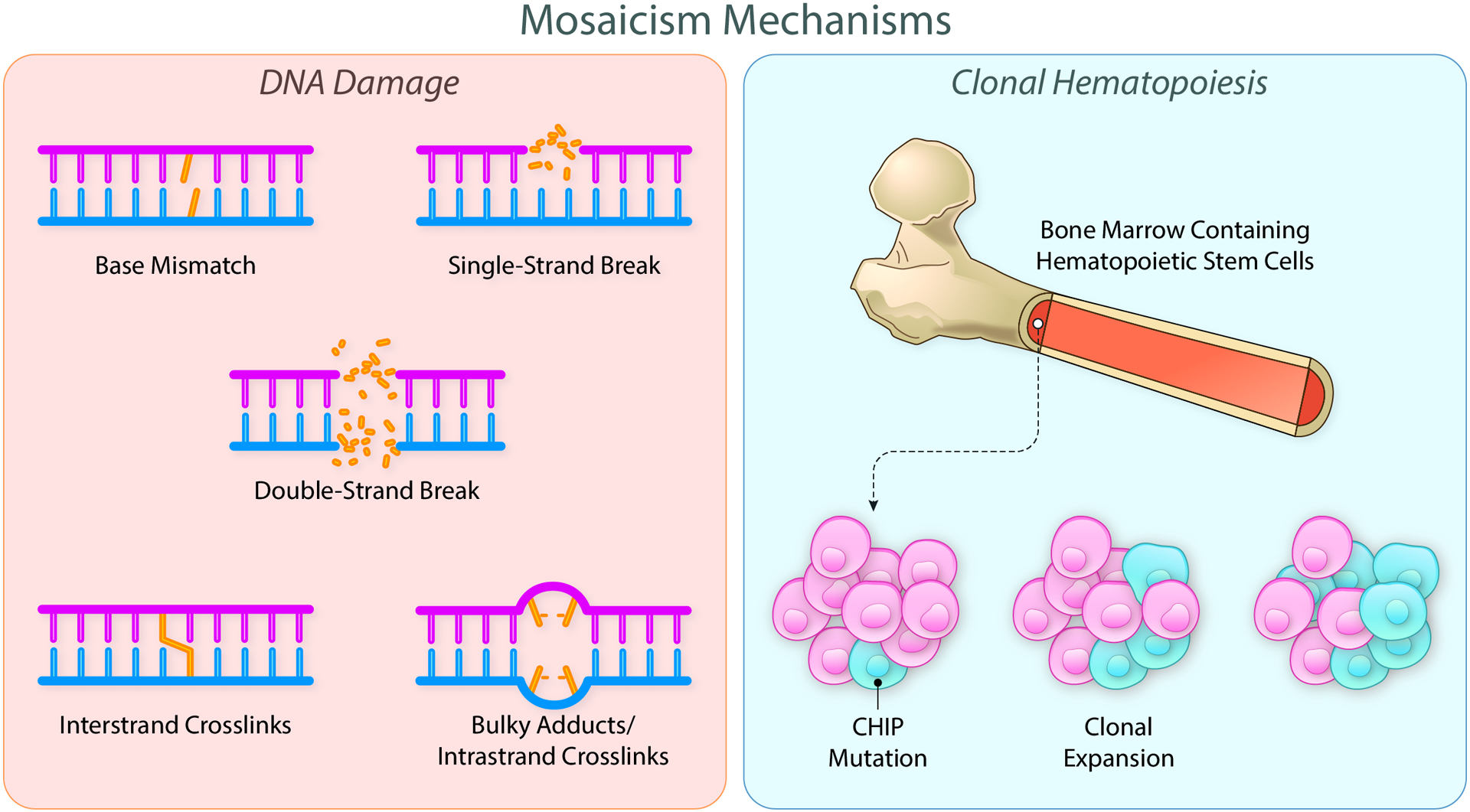
Mosaicism results from somatic DNA mutations obtained throughout the lifespan of the individual. Mutations arise from a variety of mechanisms including base mismatches, single and double strand breaks, and various crosslinks (left panel). When these mutations occur in driver genes within hematopoietic stem cells (blue cells), a survival advantage can be conferred, leading to the enhanced proliferation of the mutated cells (right panel). Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential results from this selective advantage. Created with BioRender.com. Illustration Credit: Ben Smith.
