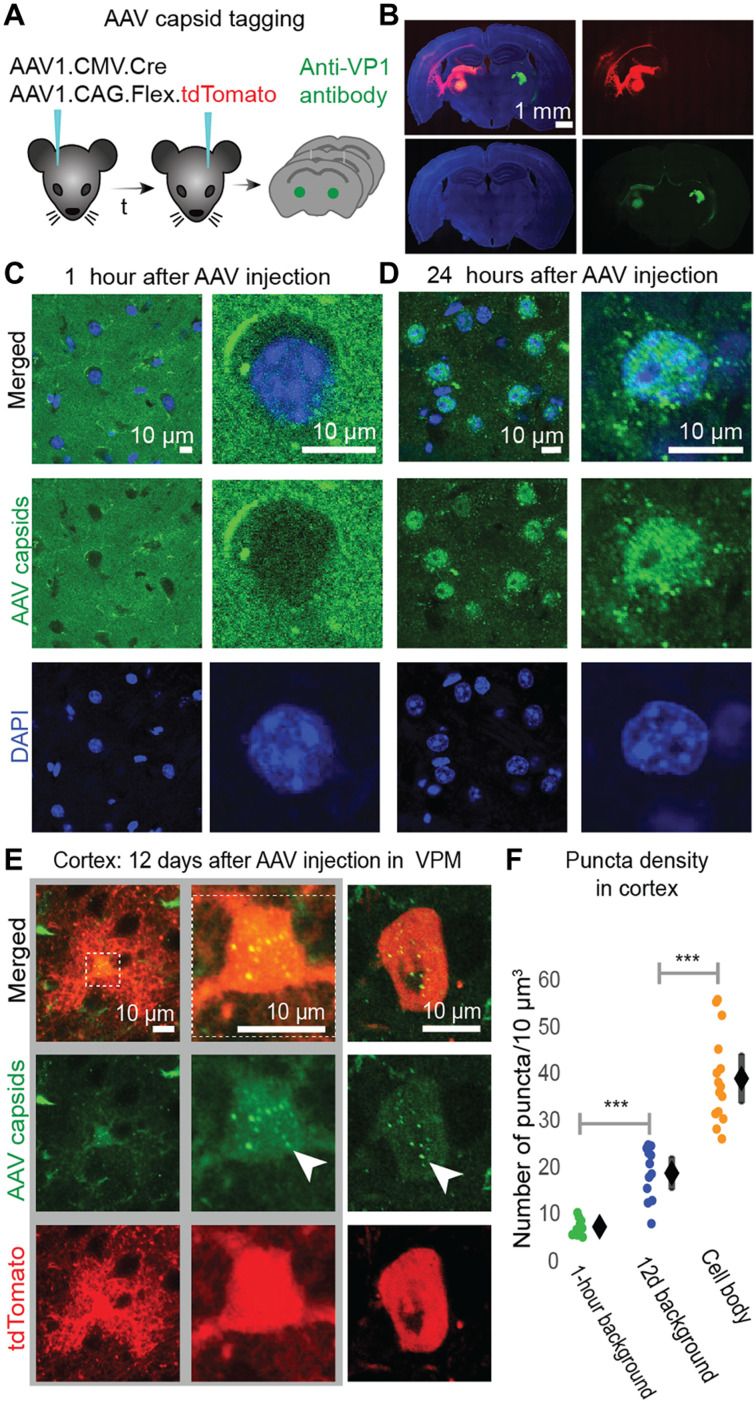
Fig. 2. Antibody-labeled AAV1 capsids localize in VPM and BX cell bodies following AAV1 injection in VPM.
(A) Schematic of AAV1 antibody-tagging experiment. One AAV1 injection [AAV1-CMV-Cre + AAV1-CAG-FLEx-tdTomato was performed in VPM (left) and one in the contralateral VPM (right, control) of the same mouse; the time delay (t) between each injection was either 24 hours (n = 3 mice) or 12 days (n = 3 mice)]. Within 1 hour of the second injection, animals were perfused and AAV capsids were tagged using anti-VP1 antibodies. (B) Coronal slice showing the two injection (in VPM) sites used in the experiment: 12 days after injection (left) and within 1 hour after injection (right). tdTomato (red) expression can be seen in VPM 12 days after AAV injection (left) but not in VPM within 1 hour of AAV injection (right), anti-VP1 antibody labeling of AAV capsids (green), and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) labeling of cell nuclei (blue). (C) AAV capsids (green) do not colocalize with VPM cell nuclei (blue) within 1 hour of AAV injection there. (D) AAV capsids (green) colocalize with VPM cell nuclei (blue) within 24 hours of AAV injection there. (E) AAV capsids (green puncta) are found in BX astrocyte (left, middle) and neuron (right) cell bodies expressing tdTomato (red) 12 days after AAV1 injection in VPM. White arrows indicate puncta. (F) Green, fluorescent puncta density in BX (L2/3 and L4) cell bodies (right) and BX background (area outside tdTomato+ cell bodies) 1 hour (left) or 12 days (middle) after AAV injection in ipsilateral VPM (1 hour background: 8.1 ± 1.2, n = 10 cells; 12d background: 19.6 ± 3.5, n = 12 cells; 12d cell bodies: 39.8 ± 5.3, n = 15 cells). Mean ± 95% CI. Unpaired two-tailed t test with significance threshold set to P < 0.05. ***P < 10−6.