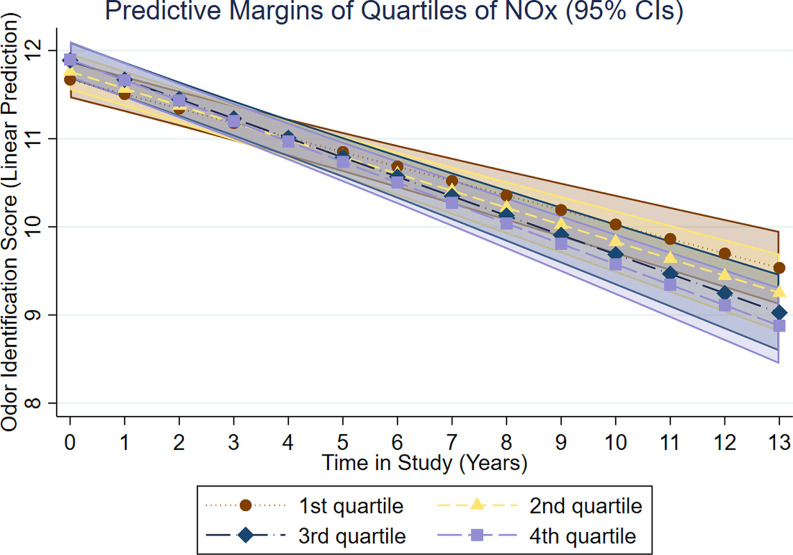
Figure 3.
Results of multiadjusted linear mixed models (adjusted for age, sex, education, odor test version at baseline, baseline assessment year, vocabulary, longest held occupation, BMI, smoking, diabetes, heart disease, and cerebrovascular disease) on associations between quartiles of air pollution in (5-y mean prior baseline assessment) and intercept and change (score/year) in odor identification in the total sample (), derived from the SNAC-K Study on Aging and Care in Kungsholmen, Stockholm, Sweden (baseline assessment between 2001 and 2003; last assessment between 2013 and 2015).