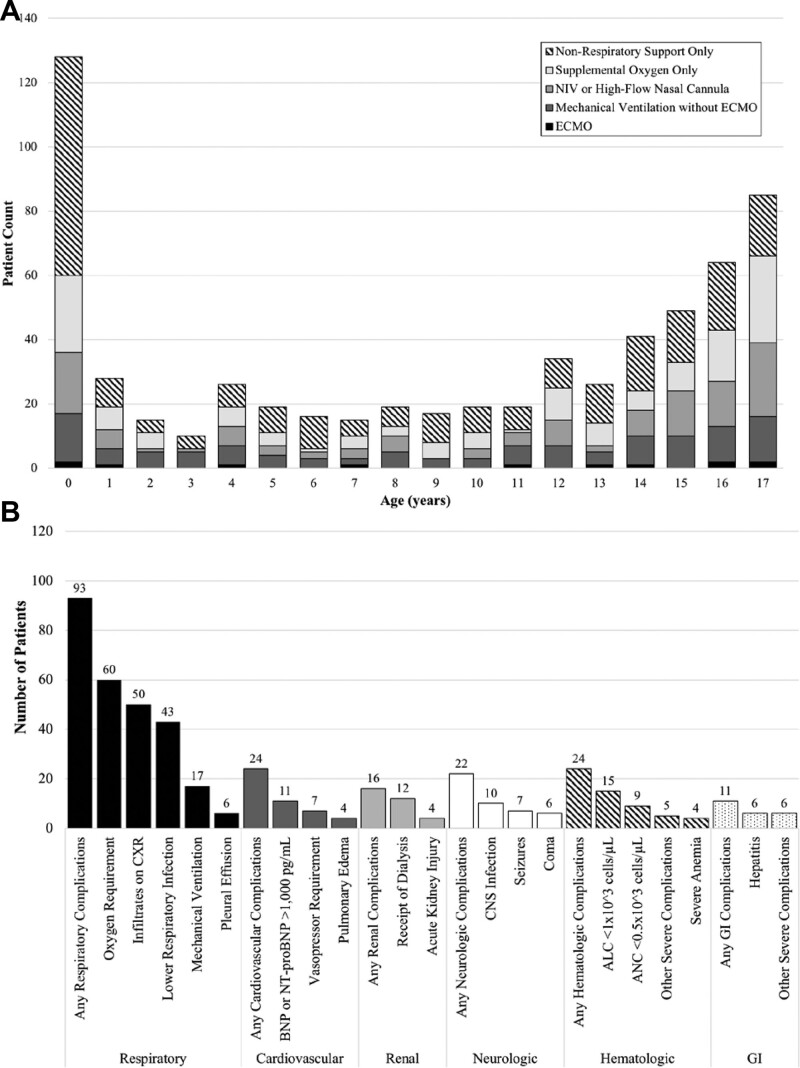
FIGURE 1.
Age distribution of patients with severe acute coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and types of complications experienced by infants with severe acute COVID-19. A: Patients >7 days to <18 years old (n = 630) with severe acute COVID-19 by age from 50 sites in 31 states, March 15 to December 27, 2020. Patients identified from Overcoming COVID-19 sentinel surveillance with positive SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction test, >7 days to <18 years of age with severe respiratory, cardiovascular, renal, neurologic, gastrointestinal, or hematologic acute COVID-19 as defined by previously outlined criteria6 (also see Table, Supplemental Digital Content 4, http://links.lww.com/INF/E610, and B, below) are shown herein. Children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) as defined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention7 and as reported previously4 were excluded from this report. Total number of patients fulfilling criteria for severe disease are shown by patient count on the y axis, with age in years shown on the x axis, with nonrespiratory involvement only, any respiratory (support), or mechanical ventilation color coded (see shading legend). By year of age, infants (128/630, 20.3%) made up a disproportionate number of severe acute COVID-19 cases among children reported to the Overcoming COVID-19 registry (A) both before August 13, 2020 (104/468, 22.2%), when inclusion was restricted to ICU/high acuity unit patients, as well as after this date (24/162, 14.8%). Of the 128 infants with severe acute COVID-19, 68 (53.1%) did not require any respiratory support, 24 (53.1%) received supplemental oxygen only, 19 (14.8%) received oxygen support through noninvasive mechanical ventilation or high-flow nasal cannula, 15 (11.7%) received mechanical ventilation and 2 (1.6%) required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Note that on August 13, 2020, the registry was restricted to patients admitted to the intensive care unit or high acuity step-down unit for patients without MIS-C, but data presented in this figure are only severe cases and, therefore, encapsulate the entire study period. B: Complications experienced by infants >7 days to <1 year of age with severe acute COVID-19 illness (n = 128 patients) from 37 sites in 26 states, March 15 to December 27, 2020. Severe COVID-19 was defined as meeting at least one of the criteria listed on the x axis. Of the total children enrolled, 242 were infants, 232 remained after adjudication to confirm that the reason for admission was due to SARS-CoV-2–related illness, with 128 of those 232 infants having fulfilled criteria for severe COVID-19. Criteria for complications were previously defined6 (also see Table, Supplemental Digital Content 4, http://links.lww.com/INF/E610), and complications by organ system detail are provided (x axis). Acute kidney injury was defined as a creatinine level equal to or above 0.62 mg/dL. Severe anemia was defined as hemoglobin level less than 7 g/dL. If fewer than 3 patients fulfilled a condition, they are not depicted herein. Also, for each patient, any instance of specific organ system involvement is represented for each category shown, with many patients meeting more than one criterion. ALC indicates absolute lymphocyte count; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; CNS, central nervous system; CXR, chest radiograph; GI, gastrointestinal; NIV, non-invasive ventilation; NT-proBNP, N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.