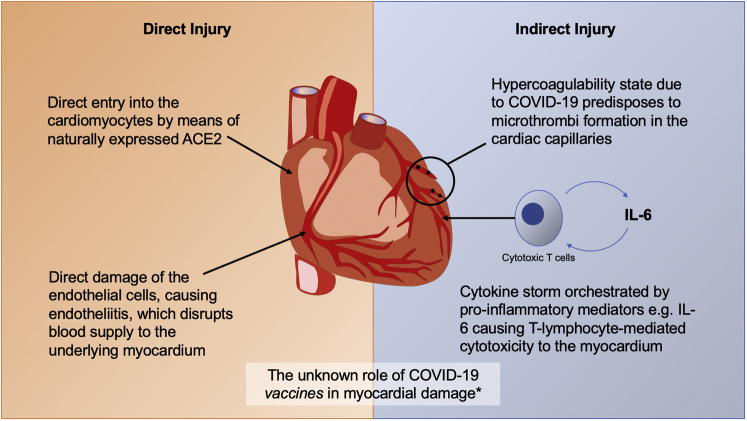
Figure 1.
Summary of the Proposed Mechanisms for Myocardial Cell Injury by SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Direct injury might be caused by cell entry via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) protein expressed naturally on cardiomyocytes or endothelial cell damage (endotheliitis) due to severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Indirect damage might be brought on by the hypercoagulability state of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), which engenders microthrombus formation, disrupting cardiac capillary flow or by means of T lymphocyte–mediated cytotoxicity as part of the phenomenon called cytokine storm. ∗Since April 2021, there have been case reports of myocarditis and pericarditis following COVID-19 vaccination across all vaccine types, especially in young male subjects. The mechanism remains unknown. IL = interleukin.