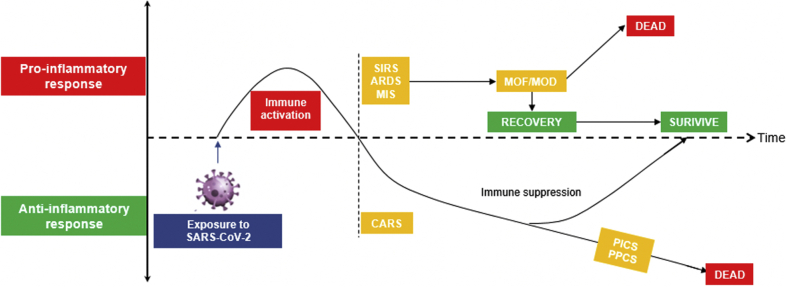
Figure 3.
Timeline of the Immune Response to COVID-19
The diagram shows the proposed immunologic reaction to SARS-CoV-2 infection, in which the proinflammatory response predominates in the acute phase, which could culminate in acute respiratory response syndrome (ARDS), multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS), or systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). Should there be no counterbalancing anti-inflammatory response, these syndromes could lead to multiorgan failure (MOF) or multiorgan dysfunction (MOD) and/or death. With adequate counteracting anti-inflammatory cytokines produced, the body is in the immune-suppressed phase, a process called compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS). With prolonged immune suppression, persistent infection can occur (ie, in the form of persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome [PICS] or persistent post-COVID-19 syndrome [PPCS]). Abbreviations as in Figure 1.