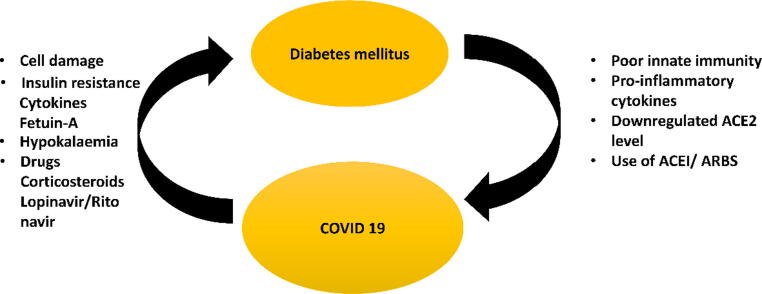
Fig. 3.
Representation of the mutual contact amongst the novel COVID-19 and DM. DM increases the seriousness of COVID-19 disease by compromising innate immunity, causing an excessive proinflammatory Cytokine reaction, and lowering ACE-2 expression. Besides, the usage ACEi/ARBs in patients with DM has been extensively linked to the intensity of disease severity in COVID-19. COVID-19, on the other hand, worsens sugar levels in persons with DM, possibly due to direct β-cell destruction mediated by viruses, increased resistance to insulin via fetuin-A and cytokines, and hypokalaemia. Furthermore, medications used to treat COVID-19, such as corticosteroids and lopinavir/ritonavir, might cause dysglycemia.