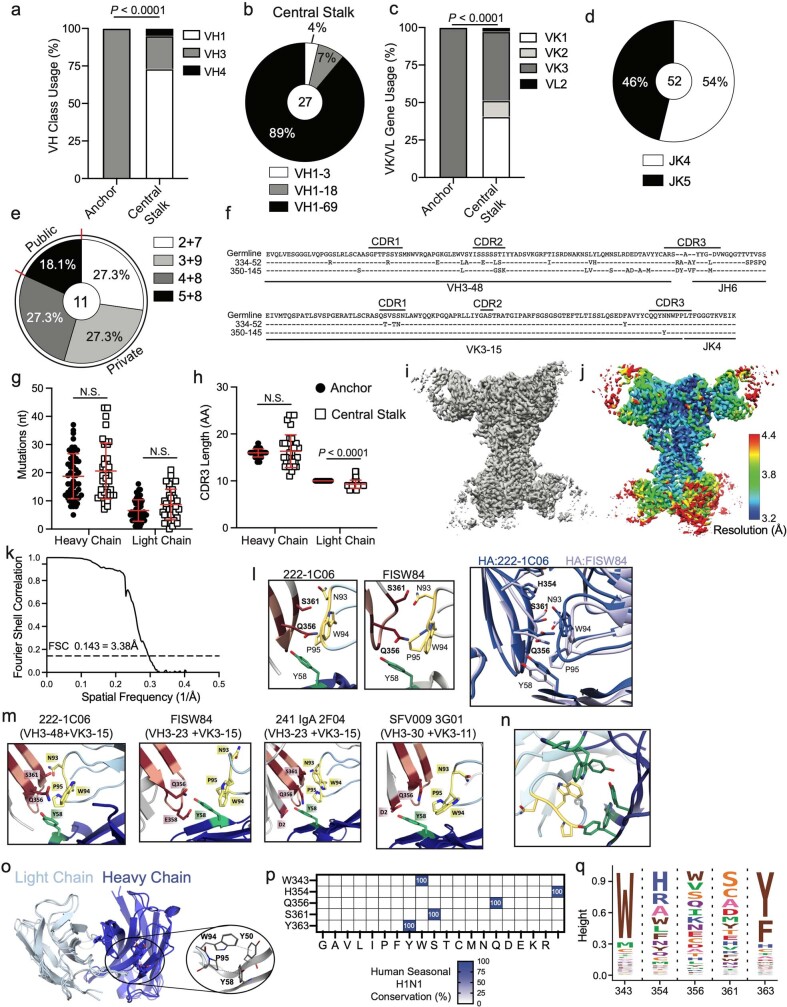
Extended Data Fig. 4. Additional repertoire and structural features of mAbs binding the anchor epitope. Related to Fig. 2.
a, VH locus usage by anchor- (n = 52 mAbs) and CS-binding mAbs (n = 37 mAbs). b, VH1 gene usage of mAbs targeting the CS epitope. c, VK locus usage by anchor- (n = 52 mAbs) and CS-binding mAbs (n = 37 mAbs). d, JK gene usage by anchor epitope-binding mAbs. e, Clonal expansions of anchor epitope-targeting mAbs. Numbers indicate heavy and light chain parings, which are described in Extended Data Table 2. f, Heavy and light chain sequences of the public clone. g, h, Mutations (g) and CDR3 amino acid (AA) lengths (h) of heavy and light chains of mAbs binding the anchor (n = 52 mabs) or CS (n = 37 mAbs) epitopes. Data are mean ± S.D. i, Cryo-EM map of 222-1C06 binding to A/California/7/2009 E376K HA. j, k, Local resolution (j) and Fourier Shell Correlation (k) of 222-1C06 binding to HA. l, Aromatic pockets of 222-1C06 binding A/California/7/2009 E376K and FISW84 binding to A/duck/Alberta/35/1976 (PDB:6HJQ; top) and overlay of epitope:paratope interaction (bottom). m, MD simulations demonstrating the K-CDR3 NWP and H-CDR2 Y58 motifs of 222-1C06, FISW84, 241 IgA 2F04, and SFV009 3G01 binding to HA A/California/7/2009 HA. For left-hand panels in l and all panels in m, HA epitope contact residues (maroon) and heavy chain (green) and light chain (yellow) antibody contact residues of anchor mAb paratopes. Peach highlighted amino acids represent the fusion peptide of HA2. n, Fab-Fab interactions of the aromatic pocket of 222-1C06. o, MD simulation of the paratope flexibility of 222-1C06, highlighting the p-stacking of H-CDR2 and K-CDR3. p, Conservation of side-chain contacts of 222-1C06 across seasonal human H1N1 viruses circulating between 1918-2019. q, Deep mutational scanning of the side-chain contacts of 222-1C06. Data in a and c were analyzed using a Chi-square test, and data in g, h were analyzed by two-tailed unpaired non-parametric Mann-Whitney tests.