FIGURE 1.
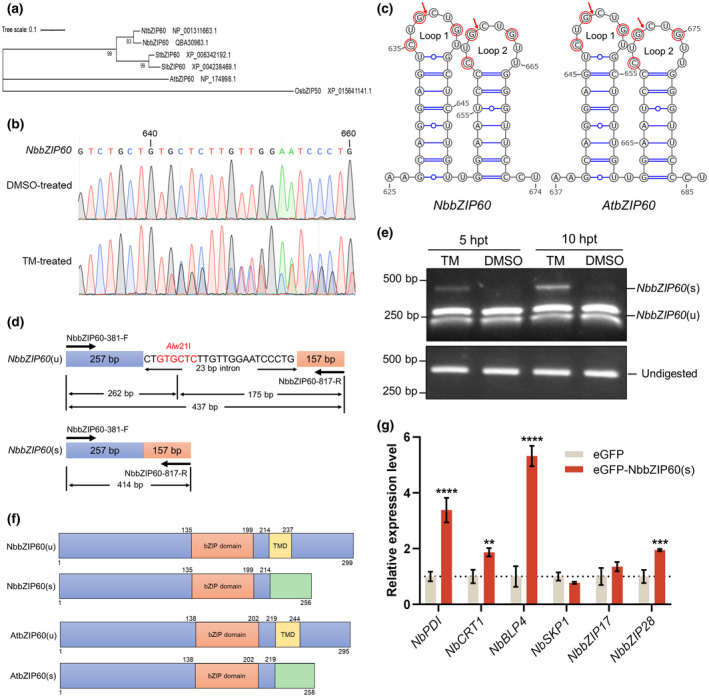
The mRNA of NbbZIP60 is spliced upon endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. (a) Phylogenetic analysis of bZIP60 proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana, tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), potato (Solanum tuberosum), Arabidopsis thaliana, and rice (Oryza sativa). The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the maximum‐likelihood method and JTT matrix‐based model. The tree is drawn to scale and the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) was performed. The GenBank accession number of each sequence is shown next to the protein name. (b) Sanger sequencing results of the NbbZIP60 cDNA in leaves of N. benthamiana treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or tunicamycin (TM). The N. benthamiana leaves were treated with 5 μg/ml TM diluted in double‐deionized water or an equal volume of DMSO as control. The total RNA of the leaf samples was extracted at 10 h posttreatment (hpt) for reverse transcription (RT)‐PCR, and the PCR products were subjected to Sanger sequencing. (c) Twin hairpin loop structures in NbbZIP60 and AtbZIP60 mRNAs at the splicing sites. Twin hairpin loop structures were predicted at the NbbZIP60 and AtbZIP60 mRNA splicing sites using the mfold web server, and the ΔG of these two structures are both −21.66 kcal/mol. Each of the two loops contains three conserved bases (red); red arrows indicate the predicted cleavage sites. (d) The schematic representation of the bZIP60 splicing assay. The primers set flanking the 23‐bp intron to amplify the cDNA of NbbZIP60(u) (top) and NbbZIP60(s) (bottom). The Alw21I cleavage site in the 23‐bp intron is indicated in red; the length of each product is labelled. (e) The splicing assays of NbbZIP60 in the TM‐ or DMSO‐treated N. benthamiana leaves. The leaves were treated with 5 μg/ml TM or an equal volume of DMSO as control. The total RNA of leaf samples was extracted at 5 and 10 hpt for the bZIP60 splicing assays. The bands of NbbZIP60(s), NbbZIP60(u), and undigested products are labelled on the right; the DNA sizes are indicated on the left. (f) Conserved domain predictions of NbbZIP60(u), NbbZIP60(s), AtbZIP60(u), and AtbZIP60(s). The predicted domains and their positions are labelled: orange box, bZIP domain; yellow box, transmembrane domain (TMD); green box, new sequence caused by splicing. (g) The RT‐quantitative PCR (RT‐qPCR) analyses of the unfolded protein response (UPR)‐related genes when expressing eGFP‐NbbZIP60(s). The eGFP‐NbbZIP60(s) or eGFP (control) was expressed in N. benthamiana leaves by agroinfiltration. The total RNA of the leaf samples was extracted for RT‐qPCR analyses at 48 h postinfiltration. NbActin served as an internal reference in relative quantification. The values represent the means of the expression levels ± SD relative to the eGFP‐expressing leaves (n = 3 biological replicates). The values were analysed by analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's test, and asterisks denote significant differences between eGFP‐NbbZIP60s‐ and eGFP‐expressing leaves (two‐sided, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001)
