FIGURE 5.
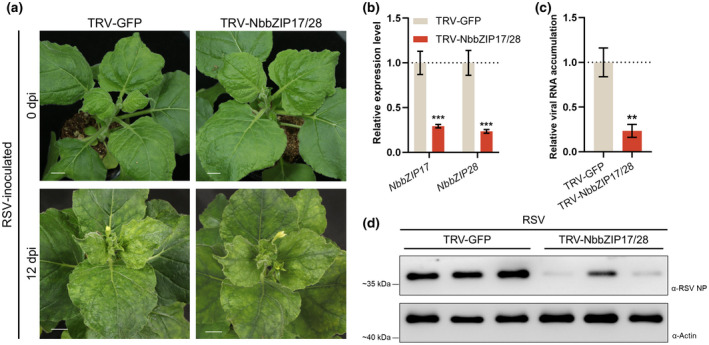
Silencing NbbZIP17/28 inhibits the infection of RSV. (a) The viral symptom of RSV on Nicotiana benthamiana plants pre‐inoculated with TRV‐GFP (control) or TRV‐NbbZIP17/28. Bars, 1 cm. (b) Reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT‐qPCR) analysis of the silencing efficiency of NbbZIP17/28 in TRV‐NbbZIP17/28 pre‐inoculated N. benthamiana. The total RNA of the leaf samples from TRV‐GFP and TRV‐NbbZIP17/28 pre‐inoculated N. benthamiana plants was extracted for RT‐qPCR analyses at 10 days postinoculation (dpi). NbActin served as an internal reference in relative quantification. The values represent the means of the expression levels ± SD relative to the TRV‐GFP control plants (n = 3 biological replicates). Data were analysed by Student's t test, and asterisks denote significant differences between TRV‐NbbZIP17/28 and TRV‐GFP pre‐inoculated plants (two‐sided, ***p < 0.01). (c) RT‐qPCR analysis of RSV viral RNA accumulation. Total RNA of leaf samples in (a) at 12 dpi was extracted for RT‐qPCR analysis. NbActin served as an internal reference in relative quantification. The values represent the means of relative expression levels ± SD relative to the mock plants (n = 3 biological replicates). Data were analysed by Student's t test, and asterisks denote significant differences between RSV‐infected and mock plants (two‐sided, **p < 0.01). (d) Western blot analysis of RSV nucleocapsid protein (NP) accumulation. The leaf samples in (a) at 12 dpi of RSV were harvested and total protein was extracted for western blot analyses. NbActin was used as a loading control. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the left
