Figure 1.
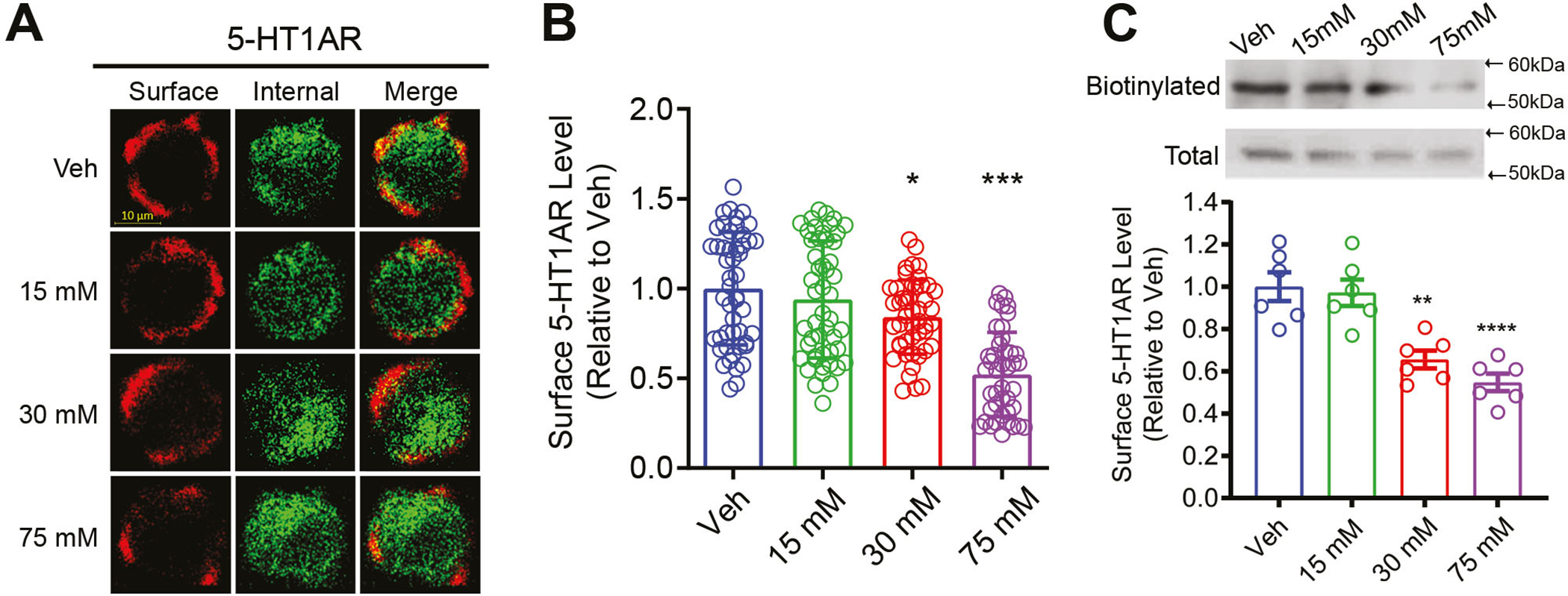
Prolonged ethanol exposure reduced surface 5-HT1AR expression in N2A cells. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of surface and intracellular 5-HT1ARs in vehicle- (Veh) and ethanol-treated cells. (B) Quantification of surface 5-HT1ARs in cells treated with Veh (N=49 cells), 15 mM (N=50 cells), 30 mM (N=47 cells) or 75 mM (N=42 cells) ethanol assessed by immunocytochemistry. Surface 5-HT1ARs were determined by a ratio of surface to total 5-HT1ARs and presented as relative to Veh. Ethanol exposure dose-dependently reduced surface 5-HT1AR levels. (C) Upper panel: representative western blot images for biotinylated surface and total 5-HT1ARs; lower panel: quantification of biotinylated surface 5-HT1AR levels in Veh- and ethanol-treated cells. Surface 5-HT1AR levels were normalized to total 5-HT1AR levels and represented as relative to Veh (N=6 replicates per group). Ethanol exposure significantly reduced surface 5-HT1AR level in a dose-dependent manner. * p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs. Veh
