Figure 2. Ceramide in microbiome-gut-liver axis.
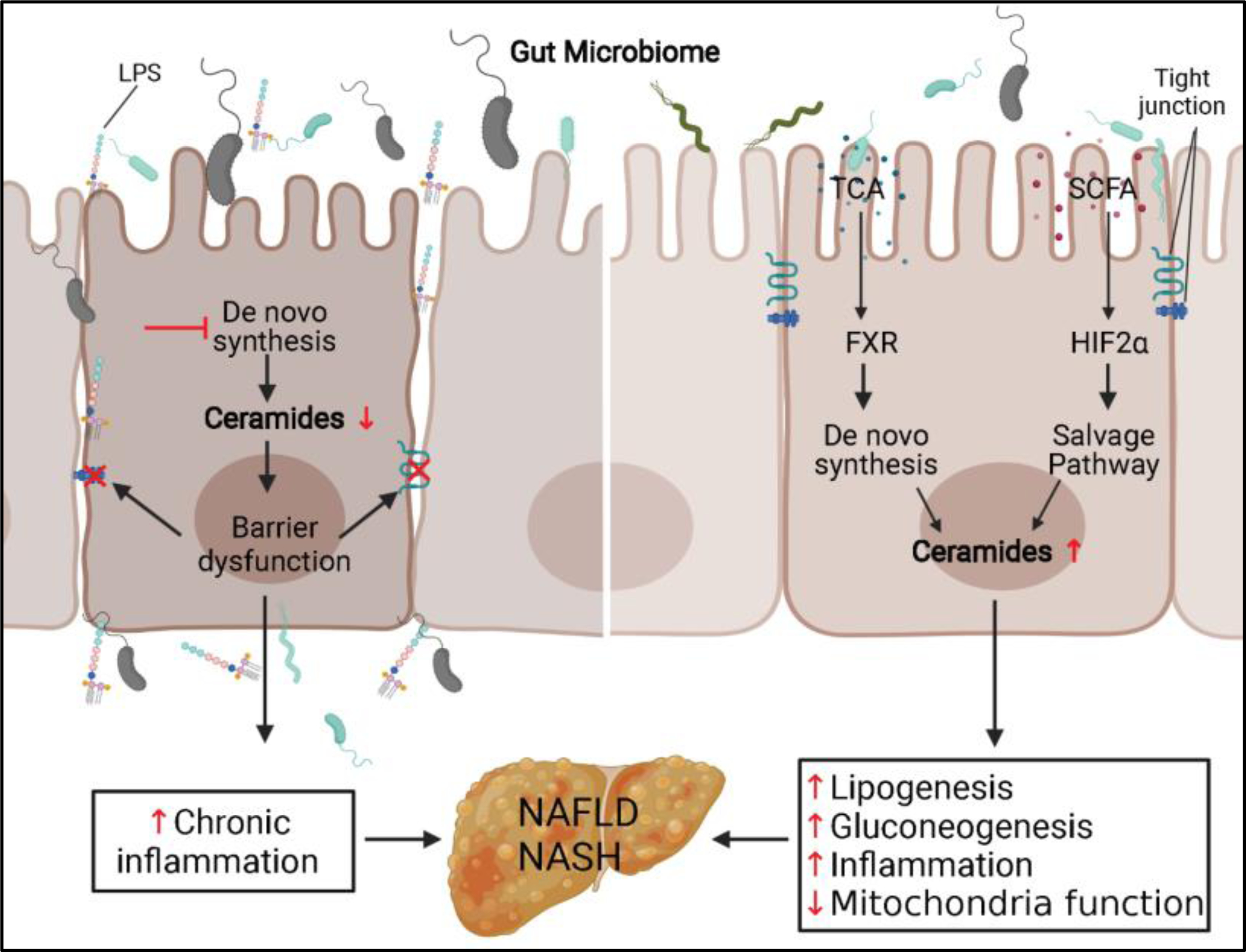
(Left) Inhibition of sphingolipid de novo synthesis pathway decreases ceramides level and leads to barrier dysfunction in the IEC. Bacteria and their metabolites infiltration in the IEC cause chronic inflammation and increase the risk of NAFLD and NASH. (Right) Schematic depiction of the role ceramides played in two pathways that microbiome regulates the metabolites in the gut lumen and causes liver steatosis and NASH. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TCA, taurocholic acid; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; HIF2α, hypoxia-inducible factor 2α; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
