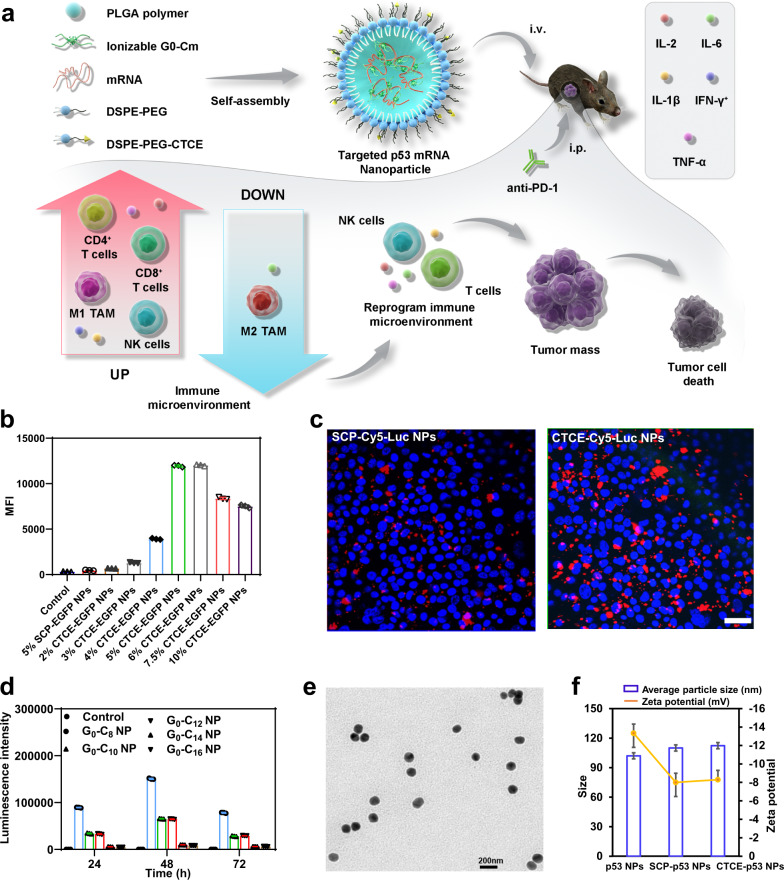
Fig. 1. CXCR4-targeted nanoparticles (NPs) for p53 mRNA delivery to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
a Schematic of CXCR4-targeted p53 mRNA NPs and combinatorial strategy using anti-PD-1 therapy to reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment for effective treatment of p53-deficient HCC. The combination of CTCE-p53 NPs and PD-1 blockade effectively and globally reprogrammed the immune TME of HCC, as indicated by activation of CD8+ T cells and NK cells, favorable polarization of TAMs towards the anti-tumor phenotype, and increased expression of anti-tumor cytokines. b Flow cytometric analysis of cellular uptake of CTCE-EGFP mRNA NPs with different CTCE peptide densities versus SCP-EGFP mRNA NPs with 5% SCP density in RIL-175 HCC cells (n = 3 cell samples/group). c Confocal fluorescence imaging of RIL-175 cell uptake of SCP-Cy5-Luciferase (Luc) mRNA NPs versus CTCE-Cy5-Luc mRNA NPs after 4 h treatment. Scale bar: 100 µm. d Effect of different cationic lipid-like materials G0-Cm on the transfection efficacy of Luc-mRNA NPs (mRNA concentration: 0.25 μg/mL, n = 3 samples/group). e TEM image of CTCE-mRNA NPs. Scale bar, 200 nm. f Average particle size and zeta potential of the p53 NPs, SCP-p53 NPs, and CTCE-p53 NPs (n = 3 samples/group). Data in b, d, and f are presented as mean values ± SD. For c and e: a representative image from one of five independent fields of view in a single experiment. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.