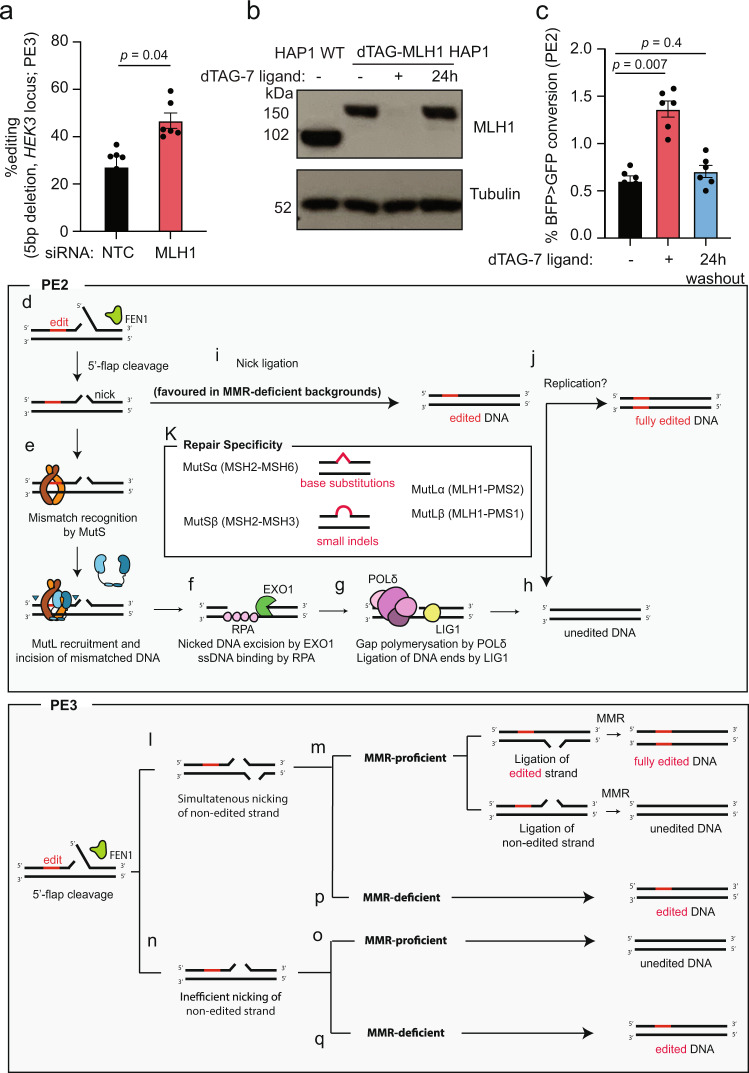
Fig. 3. Reversible ablation of MLH1 can be exploited to increase prime editing efficiency.
a PE efficiency of a 5 bp deletion (HEK3 locus) in HEK293 cells transfected with non-targeting control (NTC) or MLH1 siRNA pools. Editing efficiency measured by Sanger sequencing and TIDE analysis, for n = 3 biologically independent experiments (technical replicates also depicted). b Immunoblot for MLH1 and Tubulin in HAP1 cell extracts with (‘+’) or without (‘−’) dTAG-7 ligand. Recovery of dTAG-MLH1 expression was measured 24 h after ligand removal (‘24 h’). n = 2 biologically independent experiments. c PE2 efficiency of BFP > GFP conversion in dTAG-MLH1 HAP1 cells, untreated (‘−’), or treated with dTAG-7 ligand for 4 days (‘+’), or treated with dTAG-7 ligand for 24 h, followed by its removal for 3 days (‘24 h washout’). Data measured by flow cytometry for n = 3 biologically independent experiments (technical replicates also depicted). d–q Schematic model of MMR activity in counteracting PE efficiency. After the cleavage of the non-edited 5′-flap by the flap endonuclease (FEN1), a nick is installed in the edited strand (d). This nick is recognised by the MutS complex, after which MutL is recruited and catalysers incisions that flank the mismatch (e). Exonuclease 1 (EXO1) degrades the incised DNA and Replication protein A (RPA) coats the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) (f). Polymerase δ fills the gap and Ligase 1 (LIG1) ligates the nick (g). This repair culminates in an unedited DNA molecule (h). If the nick is ligated before mismatch recognition, an heteroduplex DNA is generated, containing the edit in one of the strands (i). The resolution of this heteroduplex potentially relies on replication (j). In PE3, the non-edited strand is simultaneously nicked (l), which directs MMR to repair the mismatch depending on which strand is ligated first (m). However, it is possible that the nicking of the non-edited strand is inefficient, leading to the MMR-mediated removal of the edit (o). In MMR-deficient backgrounds, there is ligation of the heteroduplex without removal of the edit (p, q). Statistical analysis using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test across biological replicates only. Error bars reflect mean ± s.e.m. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.