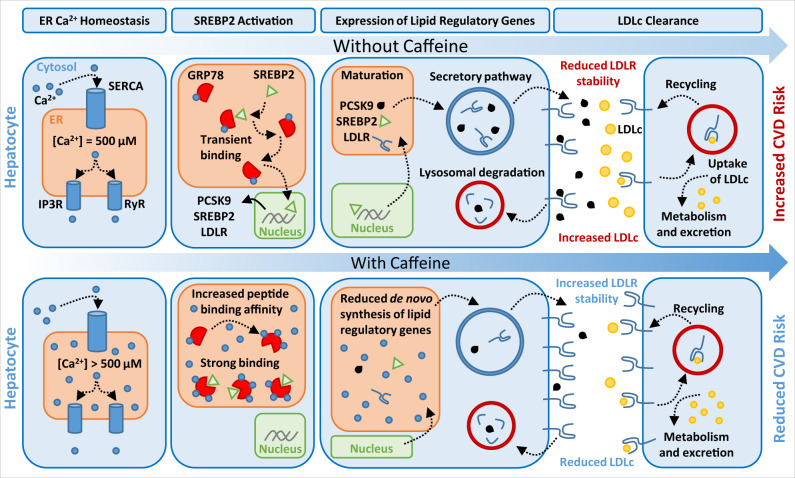
Fig. 9. Caffeine blocks PCSK9 expression and increases LDLc clearance in hepatocytes.
The treatment of liver hepatocytes with caffeine increases the concentration of ER Ca2+. Excess ER Ca2+ leads to an increase in the peptide binding capacity and chaperone activity of ER-resident GRP78. The result is an ER-resident GRP78-SREBP2 complex with enhanced stability. The failure of SREBP2 to quickly exit the ER leads to a net reduction in expression of lipid regulatory genes, including PCSK9, SREBP2 and PCSK9. With reduced outflow of de novo PCSK9, cell-surface LDLR exhibits increased half-life and abundance, leading in a net increase in LDLc clearance.