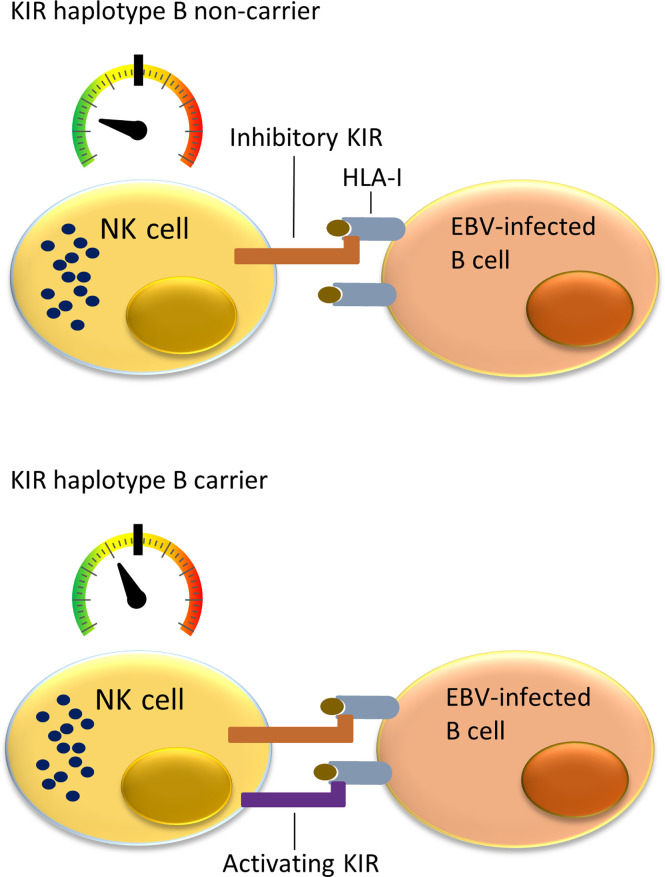
Figure 1.
Immune responses to EBV-infected B cells mediated by NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in KIR haplotype B carriers or non-carriers. NK cells in individuals not carrying KIR haplotype B often do not express a functional activating KIR receptor. The only activating KIR gene which is then present is KIR2DS4, which product ligates to a few uncommon HLA class I types and often has an allele preventing translation to protein. This means that NK cells in KIR haplotype B non-carriers have a relatively low level of stimulation (upper panel). In comparison, the multiple activating KIRs in KIR haplotype B carriers provide additional activating signals when binding to HLA class I ligand and stimulate NK cells closer to becoming fully activated and cytotoxic against virally infected cells (lower panel).