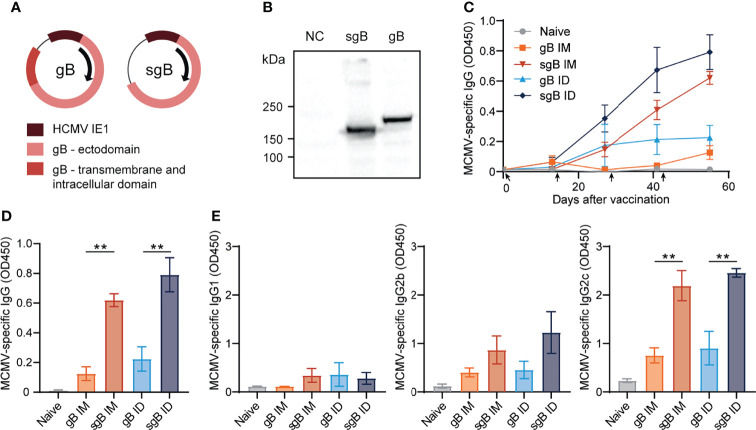
Figure 1.
Booster vaccination with DNA vaccines encoding soluble gB elicits robust IgG responses against CMV. (A) Schematic representation of the DNA vaccines encoding gB or a soluble version of gB (sgB). (B) Western blot showing expression of sgB and gB proteins following transfection of the DNA vaccines into B16F10 cells. Negative control (NC) only received the transfection agents. (C) Kinetic analysis of the MCMV-specific IgG response in serum. Mice were vaccinated intradermally (ID) or intramuscularly (IM) four times at a two-week interval with 10 µg of sgB or gB DNA vaccine. At different time points blood was taken and serum was extracted to analyze the MCMV-specific IgG antibody response. Data shown are mean values ± SEM (n=4 per group). Arrows indicate vaccine injection time-points (day 0, 14, 28, 42). (D) Presence of MCMV-specific IgG antibodies for the different vaccinations two weeks after the fourth vaccination. Experiments were performed twice with similar outcome. (E) Presence of MCMV-specific IgG1, IgG2b and IgG2c subclasses for the different vaccinations two weeks after the fourth vaccination. Experiments were performed twice with similar outcome. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis. **P<0.01.