Figure 1.
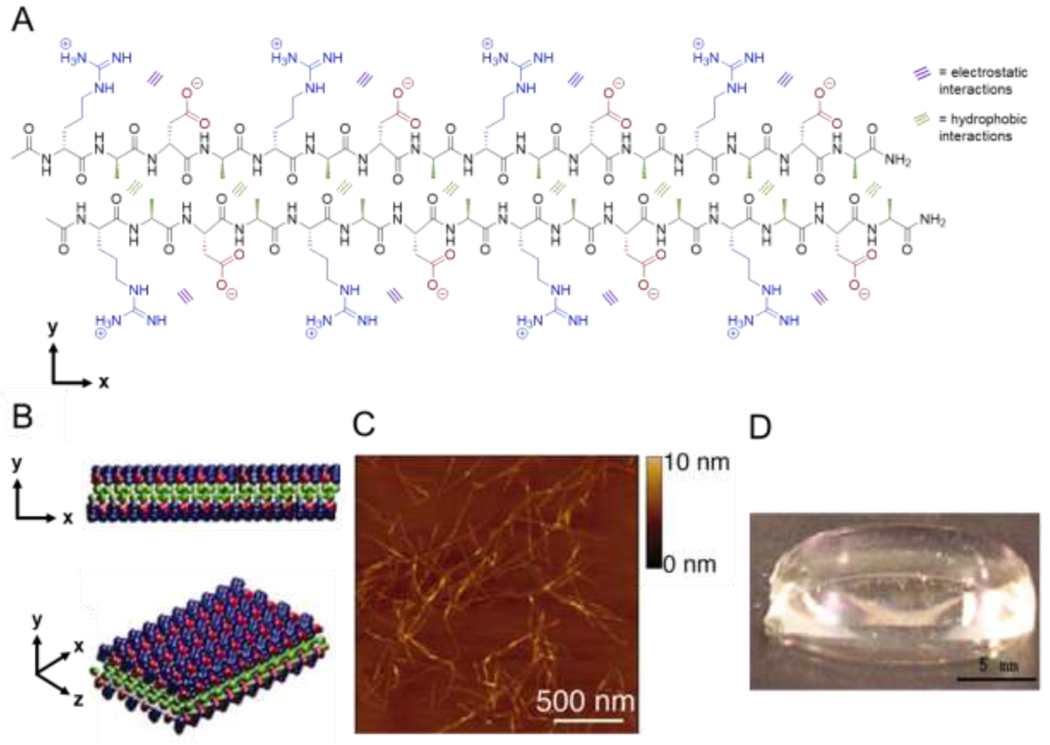
Assembly of amphipathic β-sheet peptides. (A) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding on the peptide backbone, hydrophobic interactions between alanine residues (green), and electrostatic interactions between aspartic acid (red) and arginine (blue) residues direct assembly of the amphipathic peptide RADA16 in aqueous solution. (B) RADA16 nanofibers assemble through hydrophobic interactions of alanine residues between peptides in the core of the nanofiber and electrostatic interactions between the positively and negatively charged side chains of arginine and aspartic acid residues in a checkerboard pattern on the nanofiber surface. (C) Atomic force microscopy image of assembled nanofibers. (D) Macroscopic image of a RADA16 hydrogel formed at 0.1 wt% in PBS at pH 7.5. Adapted with permission from Yokoi et al. [44], Copyright (2005) National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A.
