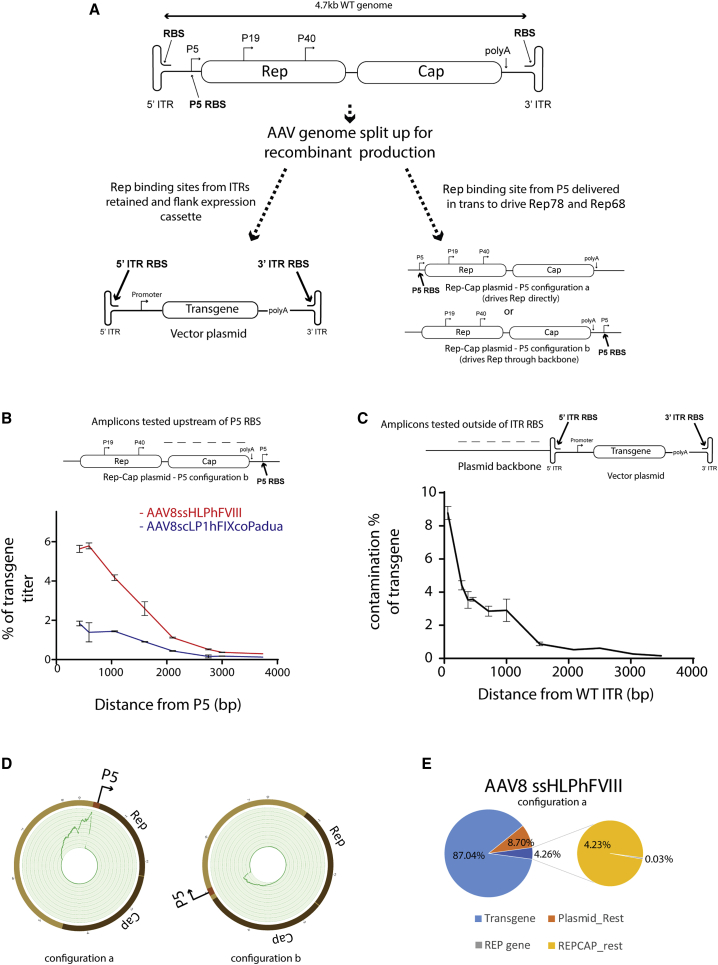
Figure 1.
Detection of transcriptionally active contaminant sequences associated with the P5-promoter packaged into AAV
(A) Schematic depicting WT (top) and recombinant (bottom) AAV genome organizations. ITR, inverted terminal repeat; RBS, Rep-binding-site; Rep, replication genes; Cap, capsid genes. Arrows denote transcriptional start sites. (B) qPCR detection of contaminant producer plasmid amplicons at increasing distance upstream of the P5 promoter Rep binding site in AAV8ssHLPhFVIII (red) and AAV8scLP1hFIXcoPadua (blue) preparations. Error bars indicate SEM. (C) qPCR detection of contaminant producer plasmid amplicons at increasing distance outside of a WT ITR in an AAV8scLP1hFIX co-preparation. Error bars indicate SEM. (D) Circos plot mapping the location of Rep-Cap plasmid reads from NGS of AAV8ssHLPhFVIII in which the P5 promoter of the Rep-Cap plasmid was positioned either directly upstream of the Rep gene (left) or moved downstream of the capsid gene (right). (E) Pie chart of NGS read contributions of producer plasmid sequences to a clinical (GMP) grade AAV8ssHLPhFVIII preparation. Left chart: light blue, reads corresponding to the ssHLPhFVIII cassette; orange, vector genome plasmid contaminants; dark blue + expanded chart, Rep-Cap plasmid contaminants (gray, AAV Rep gene contaminants; yellow, rest of Rep-Cap plasmid contaminants).