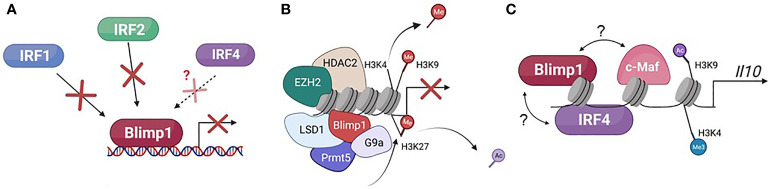
Figure 2.
Described mechanisms of gene regulation by Blimp1. (A) Blimp1 can repress target gene transcription by competing with transcriptional activators, specifically IRF1 and IRF2, and potentially IRF4, for binding to different target genes. (B) Blimp1 can repress target gene transcription by recruiting chromatin-modifying co-factors that promote suppressive chromatin structure, notably HDAC2 (histone de-acetylase 2, de-acetylates H3), G9a (lysine histone methyltransferase, H3K9 and H3K27), EZH2 (methylates H3K27), LSD1 (histone lysine demethylase, H3K4 and H3K9), and Prmt5 (di-methylates arginine residues, H2A and H4). (C) Blimp1 has been shown to activate Il10 transcription by binding directly to its locus, in a cooperative manner with IRF4, and mediating chromatin modifications that facilitate transcription (tri-methylation of H3K4 and acetylation of H3K9). Blimp1 has also been shown to cooperate with c-Maf to induce Il10 transcription in T cells, but whether or not they physically bind with each other is not known.