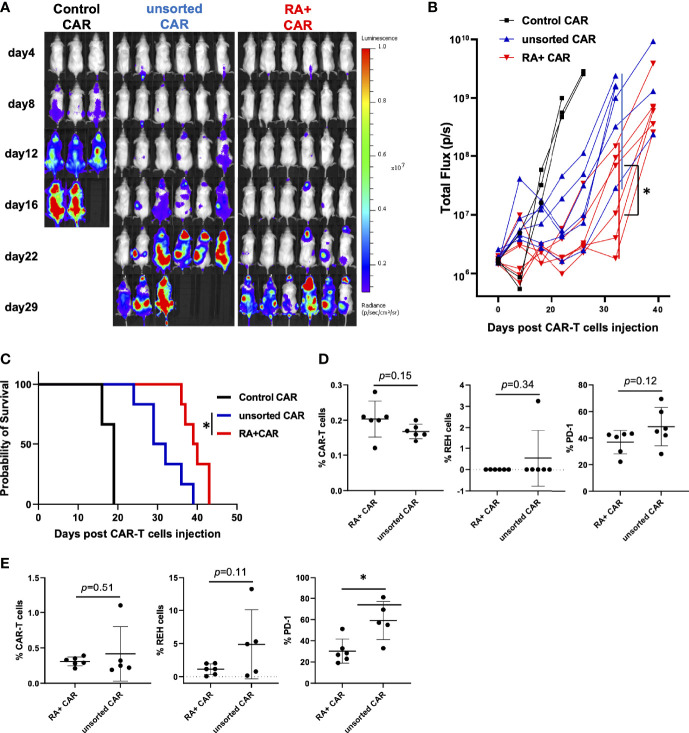
Figure 4.
CD45RA+ chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells achieved prolonged tumor control than unsorted CAR-T cells in vivo stress test. We infused 1 × 106 REH-FFLuc cells into NSG mice via the tail vein. Six days later, 1 × 105 RA+ CAR-T (n = 6), unsorted CAR-T (n = 6), or control (EPHB4) CAR-T (n = 3) positive cells were infused into the tail vein of each mouse. (A) Bioluminescence images of groups of NSG mice after intravenous CAR-T cell infusion. (B) The tumor volumes of each mouse measured as total flux (p/s) are shown. The CD45RA+ CAR-T group showed a statistically significant tumor reduction, measured as the mean total flux at day 22, compared with the unsorted CAR-T group. (C) The Kaplan–Meier plot of overall survival. The CD45RA+ CAR-T group achieved prolonged tumor control compared with the unsorted CAR-T group. Log-rank test: *P < 0.05. (D) On day 15 after CAR-T cell injection, bone marrow analysis showed CAR-T cells (left), REH cells (middle), and PD-1 expression on CAR-T cells (right) by flow cytometry. (E) On day 25 after CAR-T cell injection, bone marrow analysis showed CAR-T cells (left), REH cells (middle), and PD-1 expression on CAR-T cells (right) by flow cytometry. All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. *P < 0.05.