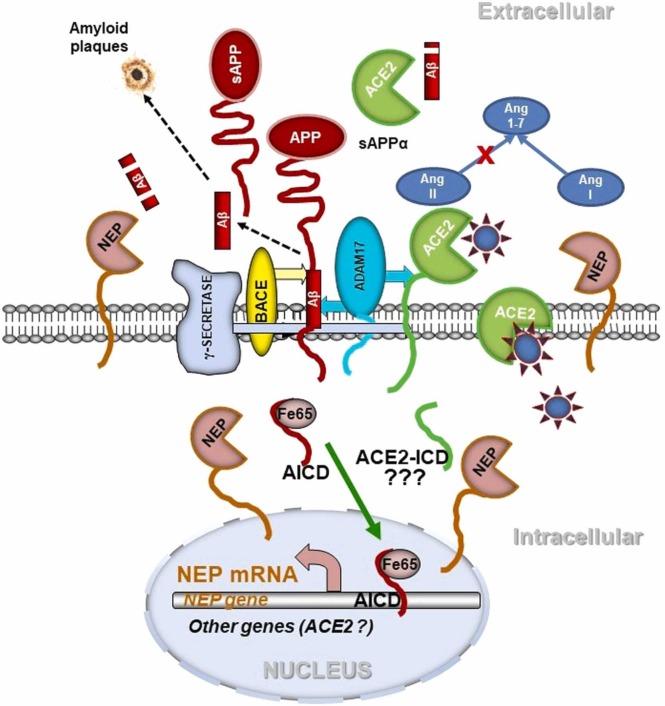
Fig. 3.
Possible mechanisms of involvement of the RAS system in angiotensin and amyloid metabolism in the brain upon SARS-CoV-2 virus infection. ACE2 in neuronal cells is involved in conversion of Ang II to Ang-(1−7) and degradation of Aβ43 peptide to Aβ42 which is further degraded by NEP. NEP also produces Ang-(1−7) from Ang I. Upon virus binding to ACE2, production of the protective Ang-(1−7) or cleavage of Aβ43 is diminished. ACE2 can be shed from the cell surface by ADAM-17. ADAM-17 also initiates non-amyloidogenic processing of APP preventing Aβ formation. The amyloidogenic pathway of APP processing, involving β-secretase (BACE) and γ-secretase, produces Aβ which can aggregate into amyloid plaques. It also releases the APP C-terminal fragment AICD, which is stabilized by Fe65 and translocated to the nucleus where it regulates gene expression, in particular of the amyloid-degrading enzyme NEP [56], [57], [58]. An ACE2 intracellular domain (ACE2-ICD) formed by γ-secretase might act similarly [110], [111].