Figure 2: Psychedelics act on the brain at multiple levels.
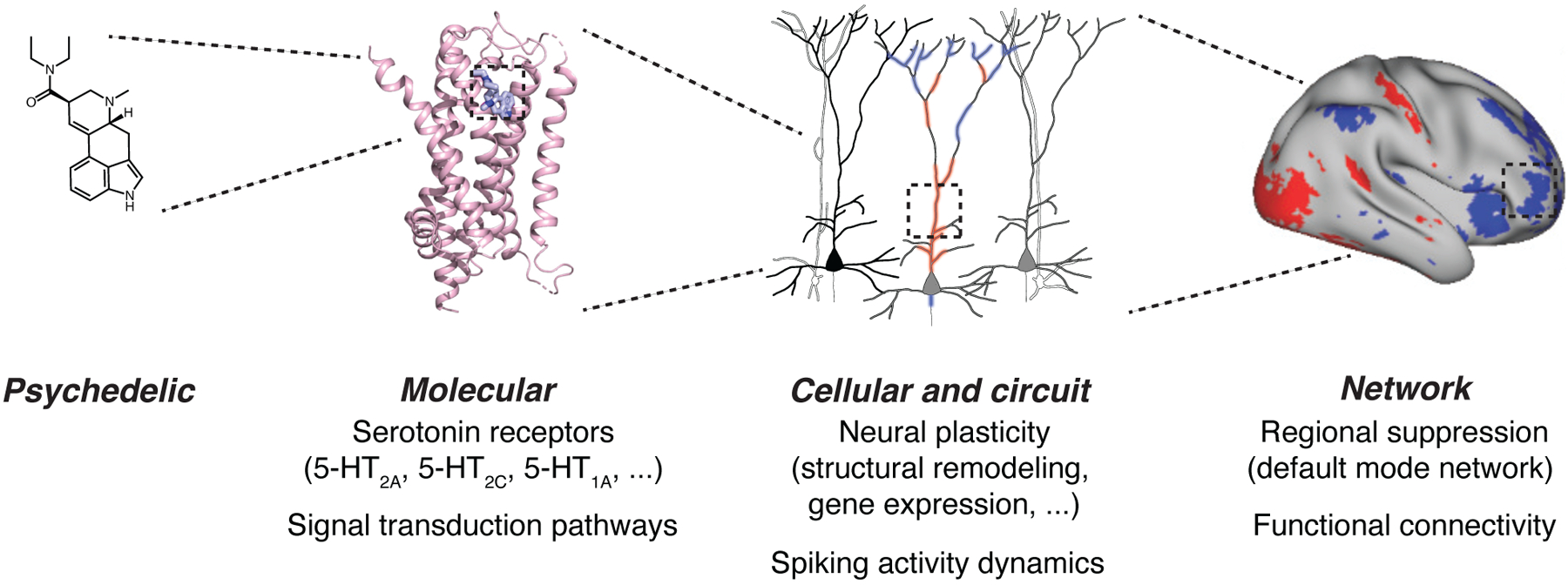
Using LSD as an example, the compound enters the brain and binds to receptors such as the 5-HT2A subtype, activating signal transduction pathways within neurons. The consequences are alterations in gene expression, neural plasticity including remodeling of the synapses and dendrites, and spiking dynamics. At the network level, these effects can be observed as brain-wide changes in regional activation and functional connectivity involving hubs such as the default-mode network. Adapted from Kim et al., Cell, 2020, Savalia et al., Trends Neurosci, 2021, Preller et al., eLife, 2018.
