Figure 1. The effects of neuronal VPS35 depletion on hippocampal neurons and glia.
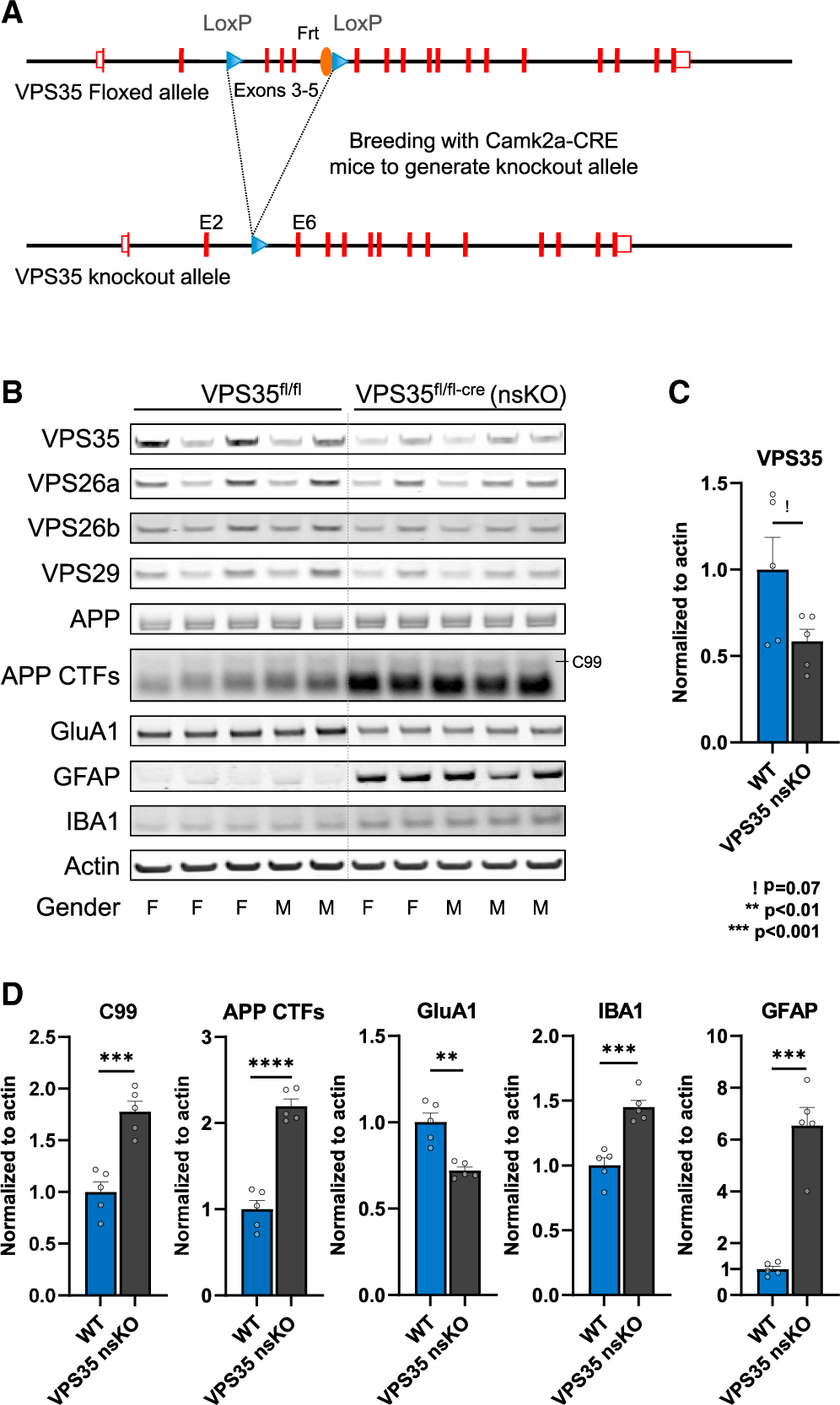
(A) Neuronal-selective VPS35 knockout mice were generated by crossing mice expressing loxP-flanked VPS35 (exons 3–5) (VPS35fl/fl) with mice expressing Cre recombinase under the Camk2α promoter. Camk2a-CRE mice were obtained from Jackson Laboratory (Stock No: 005,359).
(B) Immunoblots from of the CA1 region of WT (VPS35fl/fl, n = 5) and VPS35 nsKO (n = 5) mice (3 months of age) showing VPS35, VPS26a, VPS26b, VPS29, full-length APP, total C-terminal fragments of APP (APP CTFs), GluA1, GFAP, IBA1, and actin protein levels.
(C) Bar graph represents actin-normalized levels of VPS35 and (D) β-secretase-derived C-terminal fragment of APP (C99), total C-terminal fragments of APP (APP CTFs), and glutamate receptor ionotropic AMPA1 (GluA1), and the microglial markers ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (IBA1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).
See also Figure S1. WT = VPS35fl/fl, n = biological replicates. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ! p = 0.07, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
