Table 1.
The descriptions of cutaneous impairment variables.
| Cutaneous Impairment and Appearance of Feet According to the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument | |
|---|---|
|
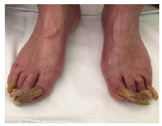
Nail diseases: diseases of the nail plate and tissues surrounding it. |
|
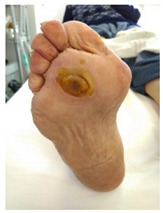
Hyperkeratosis: hyperkeratosis is caused by excessive mechanical loading. The hyperkeratosis (or callus) is thickened skin leading to a further increase in the loading of the foot, often with subcutaneous hemorrhage and eventually skin ulceration. |
|
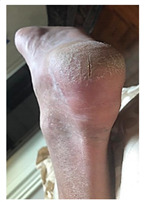
Skin care and dryness (xerosis): abnormal dryness of foot tissues caused by a lack of moisture in the skin (which can be treated by emollient therapy). |
|
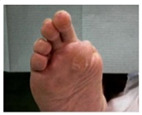
Amputation: resection of a segment of a limb through a bone or through a joint. |
|
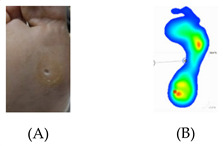
Overload areas: (A) a mechanical stress in some areas, the response to which is usually represented by a thickened skin callus; (B) peak pressures evaluated with baropodometric platform. |
|
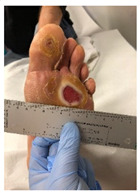
Foot ulceration: a break in the skin of the foot that involves at least the epidermis and part of the dermis. We considered the foot ulceration in people with currently or previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus. |
|
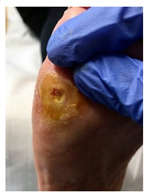
Pre ulcerative lesions: a foot lesion with a high risk of developing into a foot ulcer, such as intra- or subcutaneous hemorrhage, blister, or skin fissure not penetrating the dermis. |
