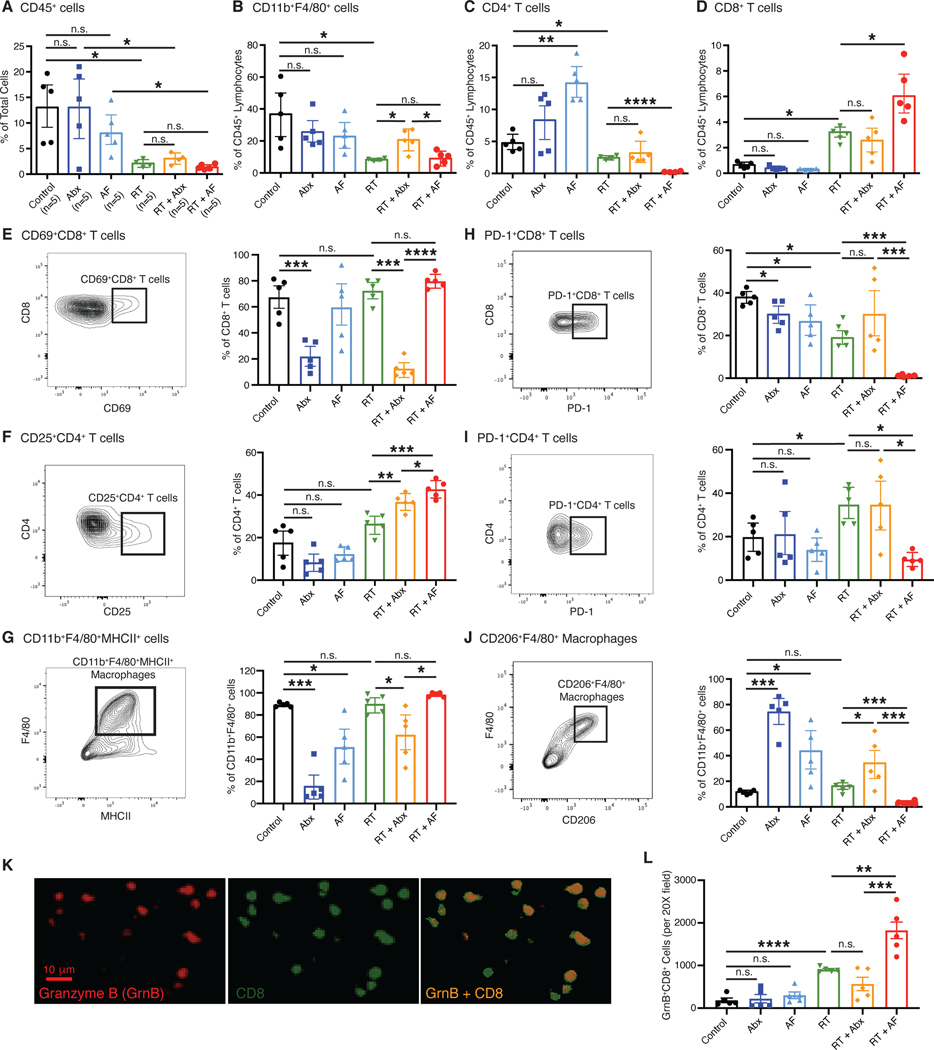
Fig. 3. Depletion of bacteria, but not fungi, decreases antitumor immunity.
Irradiated E0771 mammary tumors were harvested from mice and dissociated at one week following radiation (RT). CD45+ cells were magnetically isolated and the resulting CD45+ cells stained with fluorescent antibodies as described in Materials and Methods and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Total leukocytes (CD45+ cells), (B) CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages, (C) CD4+ T cells and (D) CD8+ T cells were assessed following antibiotic or antifungal treatment. Both activated CD69+CD8+ T cells (E), CD25+CD4+ T cells (F) and CD11b+F4/80+MHCII+ macrophages (G) and immunosuppressive PD-1+CD8+ T cells (H), PD-1+CD4+ T cells (I) and CD11b+F4/80+CD206+ macrophages (J) were examined. Tissue sections were also examined for Granzyme B (GzmB) expressing CD8+ cells (K) and (L). Significance was determined by Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction. Antibiotics (Abx) were ampicillin, imipenem, cilastin and vancomycin. Fluconazole was the antifungal agent (AF) used for these experiments. n=5 per group.