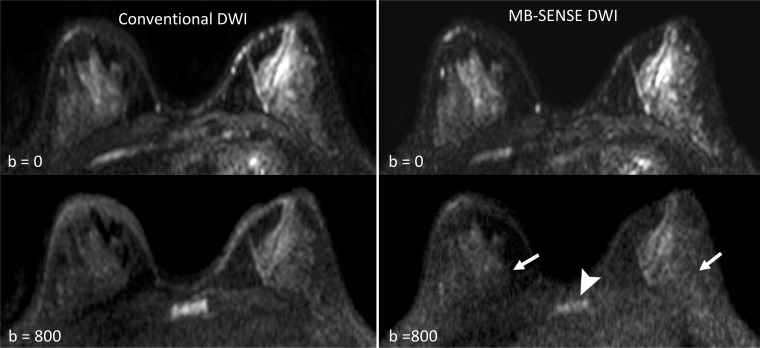
Figure 5:
Example of differences in signal quality observed on images obtained by using MB SENSE compared with images obtained by using conventional diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Posterior fibroglandular tissue regions can be better evaluated on conventional DWI acquisition (left) than on the MB SENSE DWI acquisition (right) because of the reduced signal of the MB SENSE image, most apparent on b = 800 sec/mm2 (arrows). Reduced signal is also evident in the chest wall and sternum (arrowhead) for the MB SENSE acquisition compared with the conventional DWI acquisition. One reader preferred conventional DWI, whereas the other two rated the techniques as being equal. MB = multiband, SENSE = sensitivity encoding.