Figure 3.
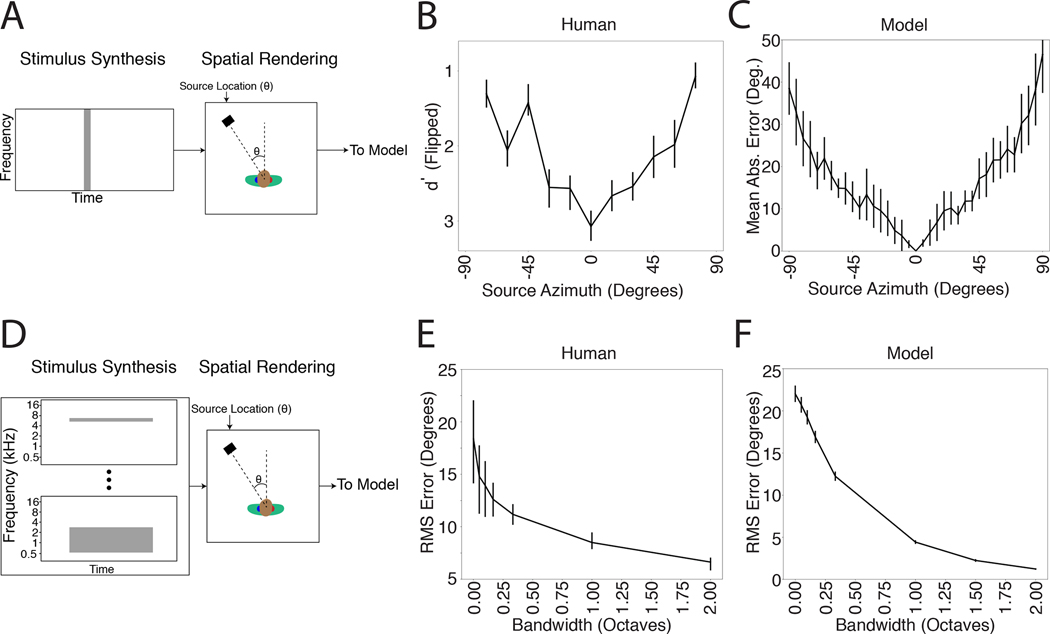
Azimuthal localization is most accurate at the midline and improves with stimulus bandwidth. A. Schematic of stimuli from experiment measuring localization accuracy at different azimuthal positions. B. Localization accuracy of human listeners for broadband noise at different azimuthal positions. Data were scanned from a previous publication80, which measured discriminability of noise bursts separated by 15 degrees (quantified as d’). Error bars plot SEM. C. Localization accuracy of our model for broadband noise at different azimuthal positions. Graph plots mean absolute localization error of the same noise bursts used in the human experiment in B. Error bars plot SEM across the 10 networks. D. Schematic of stimuli from experiment measuring effect of bandwidth on localization accuracy. Noise bursts varying in bandwidth were presented at particular azimuthal locations; participants indicated the azimuthal position with a keypress. E. Effect of bandwidth on human localization of noise bursts. Error bars plot SD. Data are replotted from a previous publication82. F. Effect of bandwidth on model localization of noise bursts. Networks were constrained to report only the azimuth of the stimulus. Error bars plot SEM across the 10 networks.