Figure 3. IL-36R-deficiency resulted in exacerbated liver damage.
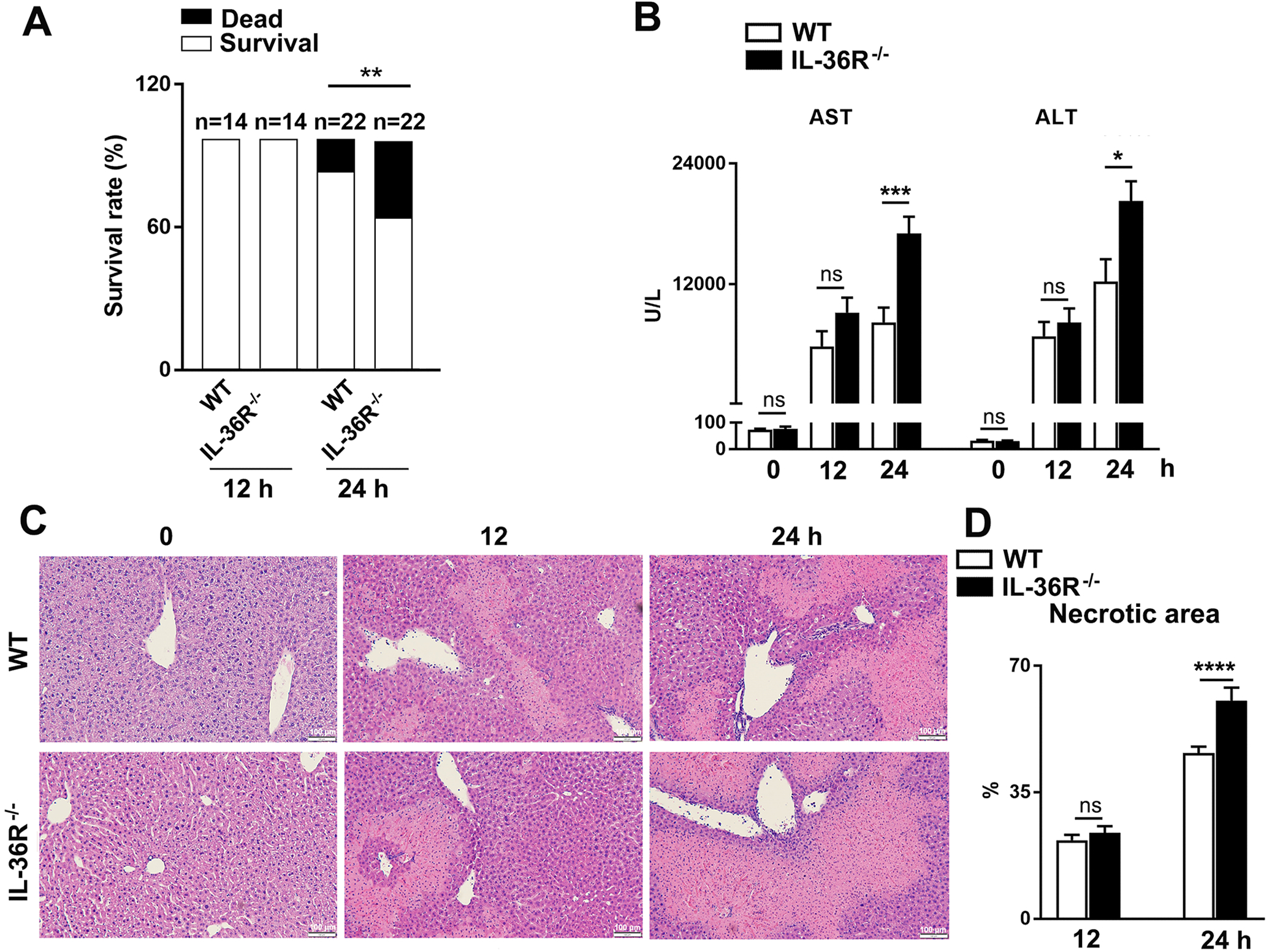
WT and IL-36R−/− mice were i.v. treated with 12 mg/kg of Con A. PBS-injected mice were used as controls (0 h). Animals were euthanatized at 12 and 24 h after Con A treatment. (A) Survival rates of WT and IL-36R−/− mice. (B) Serum ALT and AST levels. (C) Representative images of H&E staining for livers. (D) Statistical analysis of necrotic areas. n= 4–6 samples/ control group. n = 14–22 samples/ Con A-treated group from pooled experiments. The data are shown as mean ± SEM of each group from three independent experiments. Two-tailed unpaired T test was used for statistical analysis. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001; ns, no significant difference.
