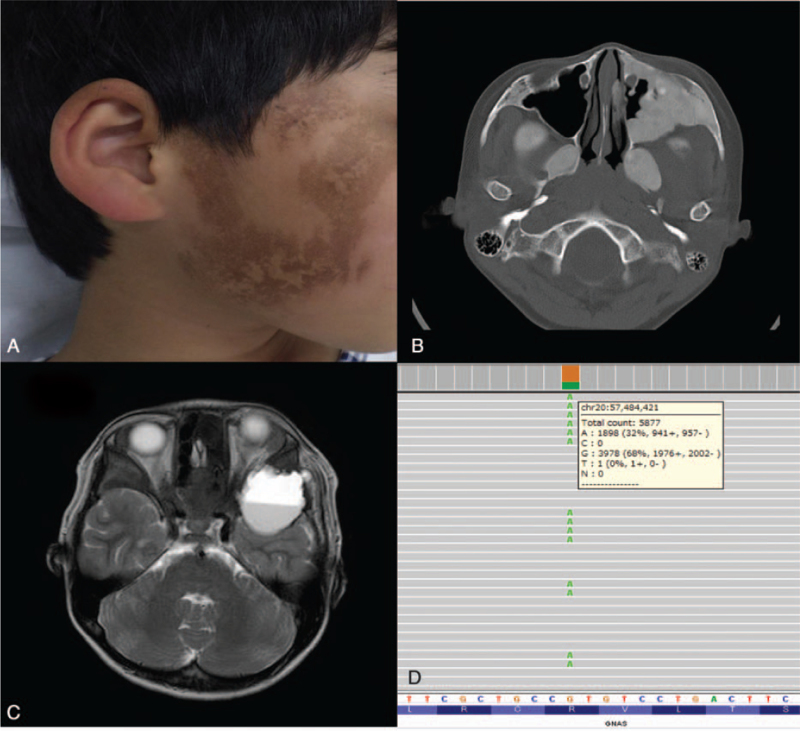
Figure 1.
Dermatological findings and radiological examination of a patient with fibrous dysplasia and aneurysmal bone cyst before treatment and genetic analysis. (A) Café-au-lait macules from birth on the right-hand side of the patient's face were identified. (B) CT revealed expansile ground-glass opacity on his bilateral pterygoid process and on the posterior wall of the left maxillary sinus (axial CT bone window of the skull base showed ground-glass opacification on his bilateral pterygoid processes and on the anterior and posterior bony walls of the maxillary sinus) and we diagnosed fibrous dysplasia. (C) Transverse T2-weighted MRI showed the cystic bone tumor with fluid-fluid level in the left middle cranial fossa with left optic nerve compression, indicating secondary ABC. (D) Genetic analysis by next-generation sequencing showed a somatic activating mutation in GNAS at c.602G > A (p.R201H) at a variant allele frequency of 32.3%. ABC = aneurysmal bone cyst, CT = computed tomography, MRI = magnetic resonance imaging.