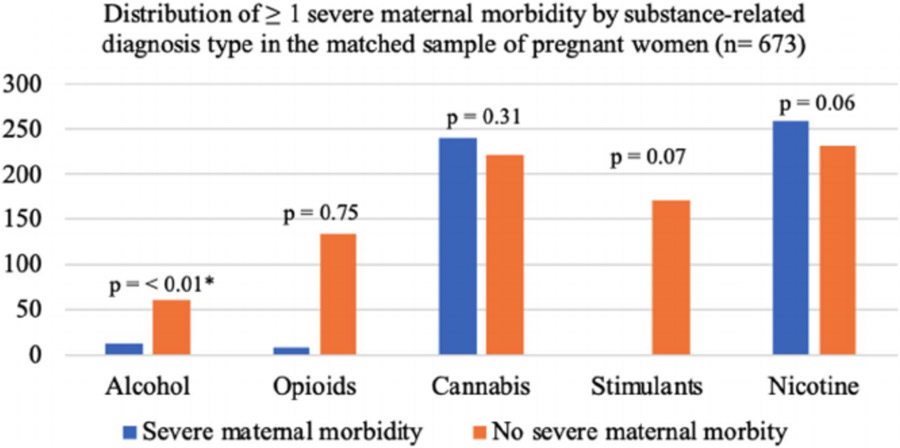
FIGURE 2.
Distribution of ≥1 severe maternal morbidity (SMM) by substance-related diagnosis type in a matched 1:1 sample of pregnant women in a large healthcare system from March 1, 2016, to August 30, 2019 (n = 673). *Having an alcohol-related diagnosis was associated with SMM (adjusted odds ratio = 3.07 [95% CI, 1.58–5.95], p-value = 0.0009). Women without a substance-related diagnosis (n = 1,252) are not included in this graph due to the unbalanced distribution of women without a substance-related diagnosis and SMM, which makes the figure difficult to interpret. However, the sample size and percentage for each substance by those with and without SMM can be found in Table 5. Note: The graph appears to visually present a significant difference between an opioid-related diagnosis and SMM. However, due to the large difference in sample size in women with and without SMM and the small sample size of women with an opioid-related diagnosis with SMM (n = 9), no significant association was observed