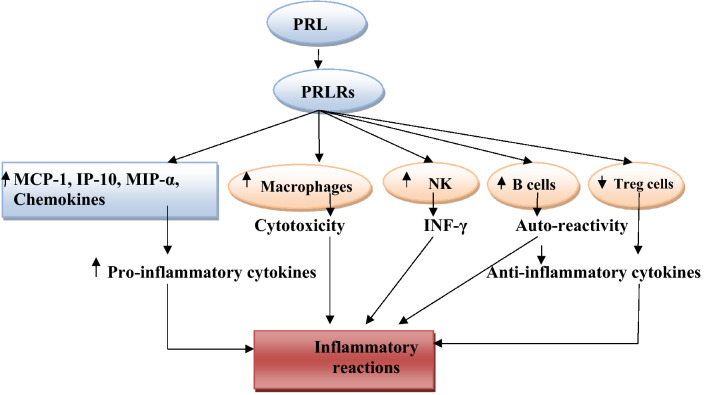
Fig. 4.
Pro-inflammatory role of prolactin (PRL): PRL through PRL receptors (PRLRs) activates release of macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), interferon protein 10(IP-10), chemokines, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1(MCP-1). PRL also stimulates natural killer (NK) cells to produce INF-γ, PRL inhibits function of regulatory T cells (Treg), and PRL alters B cells function and promotes auto-reactivity and antibody production with subsequent inflammatory reactions