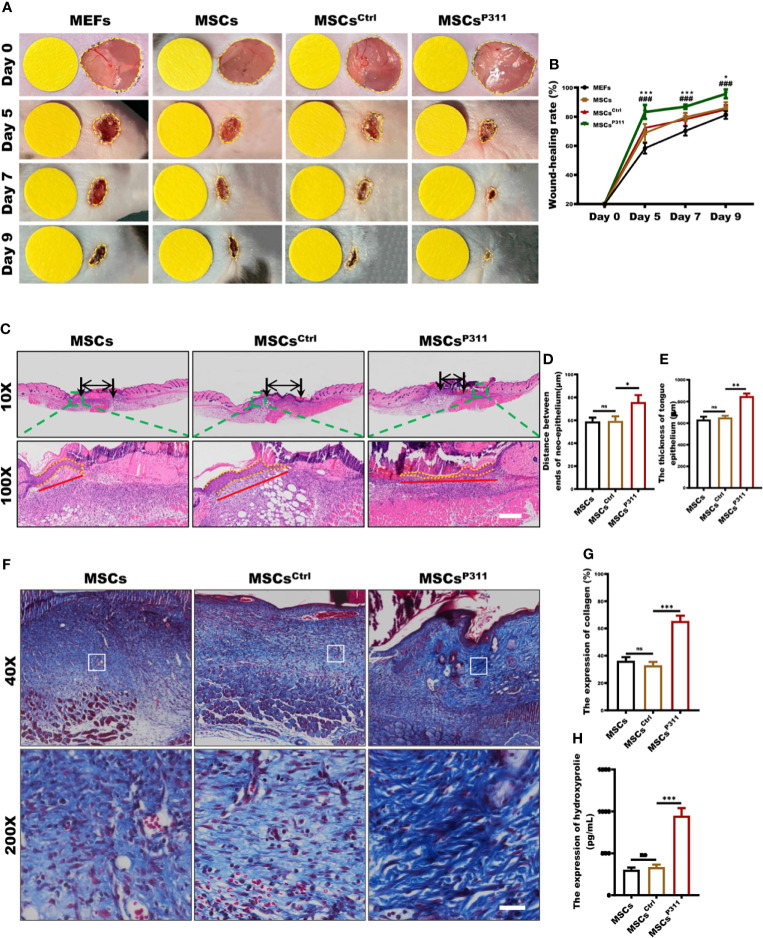
Figure 1.
P311 could enhance the capability of MSCs-mediated promotion of skin wound repair. Full-thickness wounds were created on both sides of the dorsal skin in sex- and age- matched C57BL/6 mice. Wound closure kinetics in mice subcutaneously injection with 1×106 MEFs, MSCs, MSCsCtrl or MSCsP311 after wounding immediately (n=3/group) was analysed. (A, B) Representative photos of wounds on 5, 7 and 9 days post-wounding were shown (left panel). The open wound area was normalised to 1cm-diameter yellow circle which was the same size as the area of wound on day 0, and wound closure curve was statistically analysed (right panel). (* means MEFs vs MSCs) (C–E) The re-epithelialisation of wounds on day 7 post-excision was determined by H&E staining in mice with MSCs, MSCsCtrl, or MSCsP311 administration (n=3/group). Representative H&E images of re-epithelialisation were shown, and the distance between ends of neo-epithelium (black arrows), the length (red solid line) and thickness (yellow dotted line) of neo-epithelial tongue were statistically analysed, respectively. Scale bar: 200 µm. (F, G) Representative Masson images of granulation tissue were shown, and the expression of total collagen with blue staining was statistically analysed. Scale bar: 50 µm. (H) The contents of HYP were examined and analysed in wound tissues. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments and represent mean ± SD of indicated number of mice per group. (ns, no statistical significance; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***,###P < 0.001).