Figure 3. Formulation and Genetic Engineering Strategies to Improve LBP Delivery.
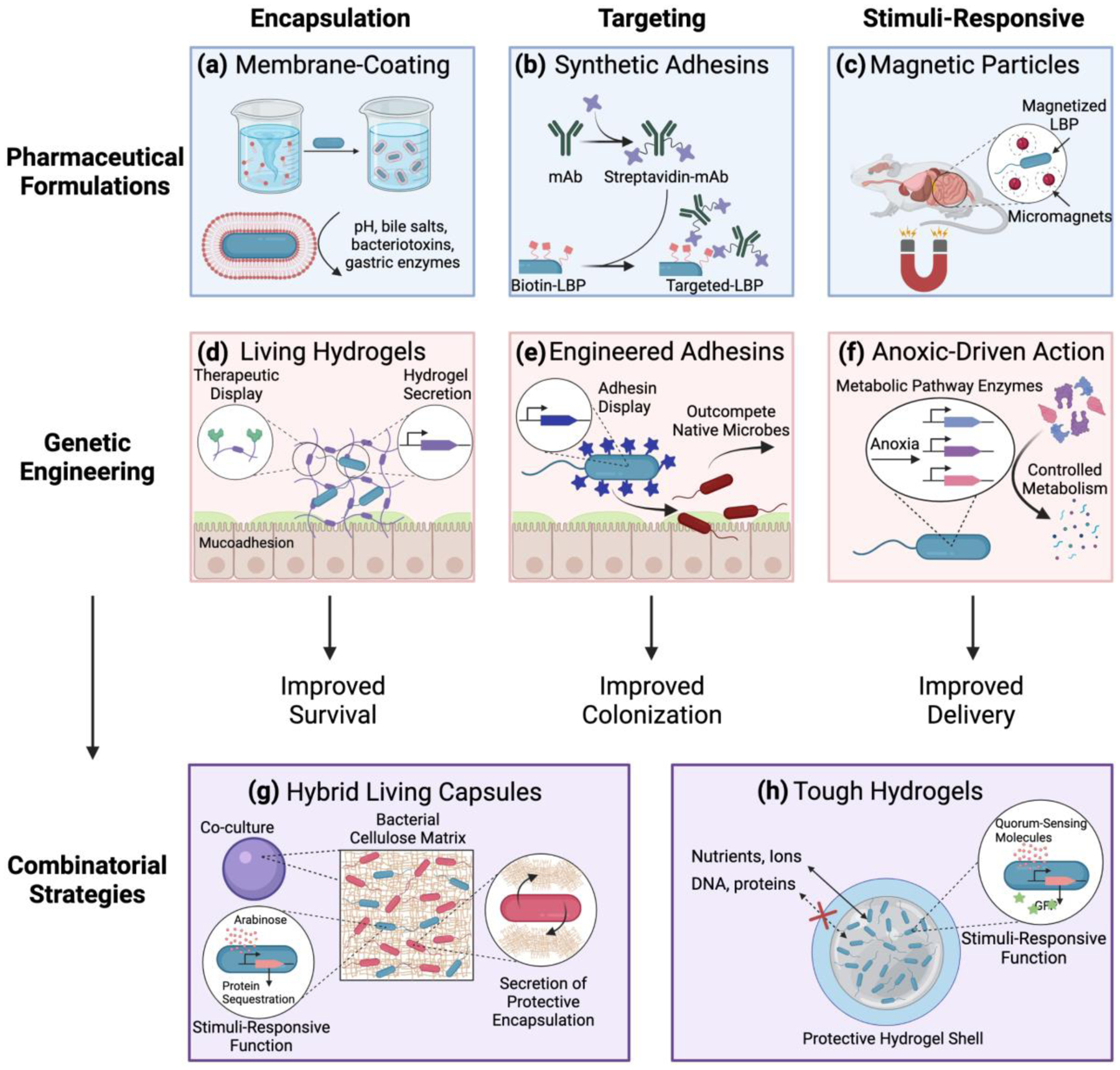
Pharmaceutical formulations and genetic engineering strategies can be leveraged to both overcome physiological challenges and utilize physiological microenvironments to improve LBP delivery and LBP function. Examples of pharmaceutical formulation approaches include (a) encapsulation via phospholipid bi-layer membrane LBP coatings, (b) targeting via synthetic adhesin-surface modification of the LBP, and (c) endowing stimuli-responsive functions by using external magnets to direct the movement of magnetized LBPs. Examples of genetic engineering approaches include (d) engineered LBPs which secrete an encapsulating protective and mucoadhesive hydrogel with conjugated therapeutic modalities, (e) LBPs engineered to express adhesins with high binding affinities on the microbial surface for targeting, and (f) the expression of several enzymes for controlled metabolism in response to anoxic conditions for stimuli-responsive therapeutic function. Recently, pharmaceutical formulations and genetic engineering strategies have been combined to (g) encapsulate genetically engineered LBPs in a hydrogel bead which allows diffusion of nutrients into the bead to maintain the engineered function while achieving biocontainment, and (h) enable co-culture of a bacterial cellulose-secreting probiotic organism with engineered LBPs to enable protective encapsulation of the LBP while maintaining its engineered function.
