FIGURE 1.
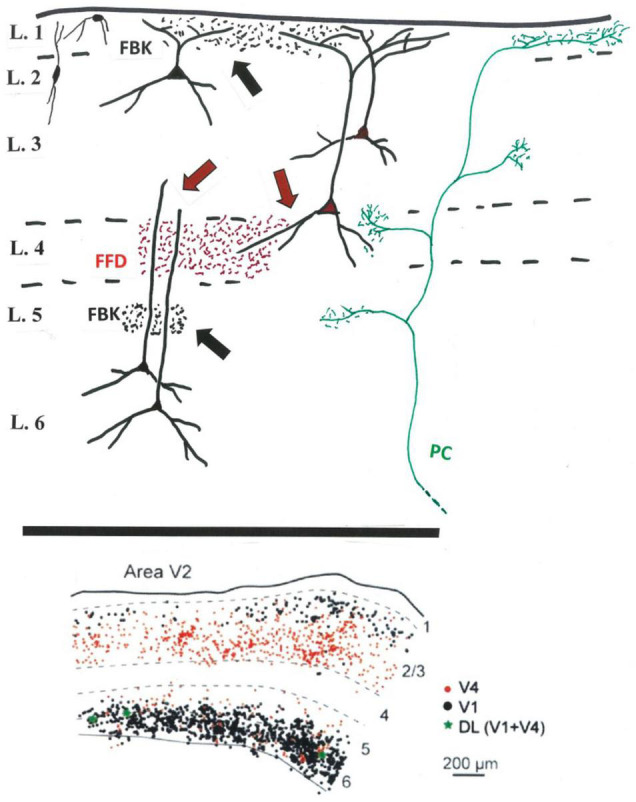
Above: Schematic sketch (V2) of FFD (in red) and FBK terminations (in black) in relation to potential postsynaptic dendrites (black) of FFD (red soma) and FBK (black soma) projecting neurons. FFD teminations in layer 4 (red arrows) potentially contact small pyramidal cells or interneurons in layer 4, basal dendrites of FFD neurons, and distal dendrites of FBK neurons. FBK or other terminations in the infragranular layers (black arrow) might access more proximal apical dendrites of infragranular neurons. Included for reference, a typical, multilaminar pulvino-cortical (PC) axon (in green) (And see Federer et al., 2021: terminations in V1 after viral infection of V2). Not shown: layer 5 neurons, inhibitory neurons (except for the representative neurons at upper left), intra- and interlaminar intrinsic connections, and the additional afferent inputs to layer 1 or other layers. Below: Predominant segregation of FFD (in red) and FBK (in black) projecting neurons in V2, as demonstrated by double retrograde injections in V1 and V4, with a small number (in green) of double labeled (DL) neurons (modified from Figure 10 in Markov et al., 2014b).
