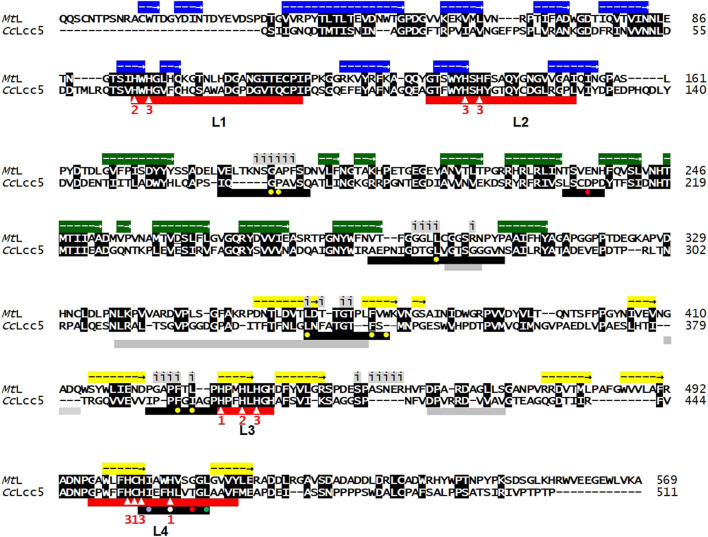
FIGURE 1.
Sequence alignment of asco-laccase MtL (AEO58496) and basi-laccase CcLcc5 (DAA04510). Conserved amino acids are shown with white letters in black boxes. The three cupredoxin-like domains are marked above the MtL sequence with arrows in colored boxes for extension of their helical structures (blue; cupredoxin-like domain 1; green: cupredoxin-like domain 2; yellow: cupredoxin-like domain 3), according to Ernst et al. (2018). Residues located at the unique dimerization interface in the asco-laccase MtL are marked above the alignment with letter i (for interface) underlain in grey (Ernst et al., 2018). Red bars beneath the alignments mark the conserved laccase signature sequences L1 to L4, with 10 conserved histidines and a conserved cysteine indicated by white triangles within the bars. Numbers 1, 2, and 3 beneath show the ligands for binding of T1, T2, or T3 copper. Black bars mark the loops forming the substrate pocket in the folded proteins (Hoegger et al., 2006; Kilaru et al., 2006; Kües and Rühl, 2011; Ernst et al., 2018). The hydrophobic residue Leu in L4, regarded as an indicator for enzymes with medium-redox-potential (Hoegger et al., 2006; Kües and Rühl, 2011), is marked in the black bar by a filled green circle. Yellow filled circles in black bars stand for hydrophobic residues that line the T1-Cu pocket of MtL, the white and red filled circles for His508 and Glu235 for the polar recognition motif of MtL for phenolic substrate (DMP) deduced in analogy from the established structure of DMP-bound M. albomyces laccase MaL, and a light-blue filled circle for a further hydrophobic ligand in the sequence of motif L4 (after Ernst et al., 2018). Grey bars underneath the alignments show sequences for the proposed alternative binding site for non-phenolic ABTS on the surface of folded MtL with an unusual hole localized 26 Å from the T1-Cu pocket (Ernst et al., 2018) in analogy to Bacillus subtilis CotA laccase (Liu et al., 2016).