Fig. 6.
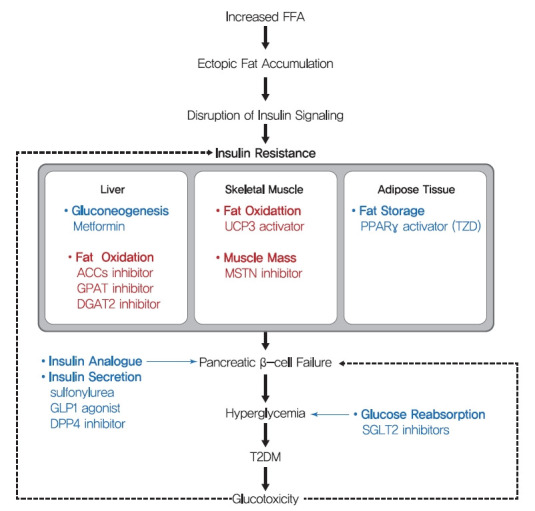
Schematic mechanism of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and therapeutic strategies for insulin resistance. The main strategies of present (blue) treatment for T2DM and possible future (red) treatments for insulin resistance are summarized. Many T2DM drugs, such as sulfonylureas, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists, and dipeptidyl peptide-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, target the ability of β-cells to secrete insulin. In addition, thiazolidinediones (TZDs) and metformin are insulin-sensitizing antidiabetic drugs, targeting fat storage capacity of adipose tissue and glucose production in liver, respectively. Key strategies of potential future treatment for insulin resistance suggested in this study are targeting enhancement of β oxidation in liver and skeletal muscle and stimulation of muscle quality. FFA, free fatty acid; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; GPAT, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; DGAT2, diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2; UCP3, uncoupling protein 3; MSTN, myostatin; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2.
