FIGURE 3.
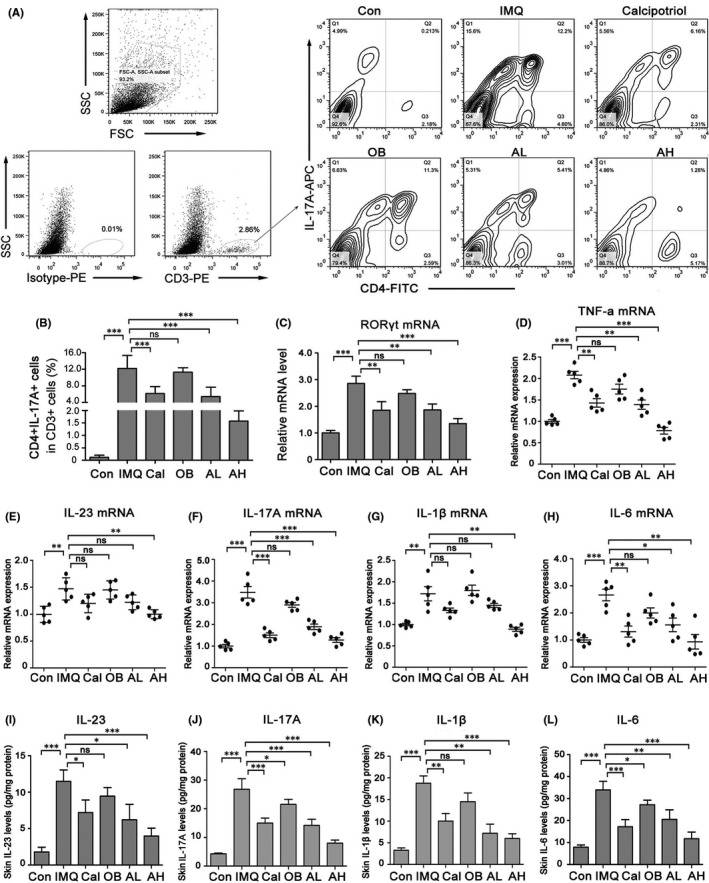
Topical astilbin decreased IMQ‐induced Th17 cell differentiation and skin inflammation in mice in a dose‐dependent manner. (A) Representative images of flow plot showing staining for CD4+IL‐17A+ T cell expression in CD3+ cells of mouse back skin in different groups. (B) The rate of CD4+IL‐17A+ T cell expression in CD3+ cells was analysed statistically. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 5). (C) RORγt mRNA expression in IMQ‐induced skin lesions. (D–H) RT‐PCR for relative expression of TNF‐α, interleukin (IL)‐23, IL‐17A, IL‐1β and IL‐6 mRNAs in the different treatment groups. Values are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 5 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs. IMQ group). (IL) ELISA was performed to assess the concentration of IL‐23, IL‐17A, IL‐1β and IL‐6 in mouse back skin of different groups. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. (n = 5, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001)
