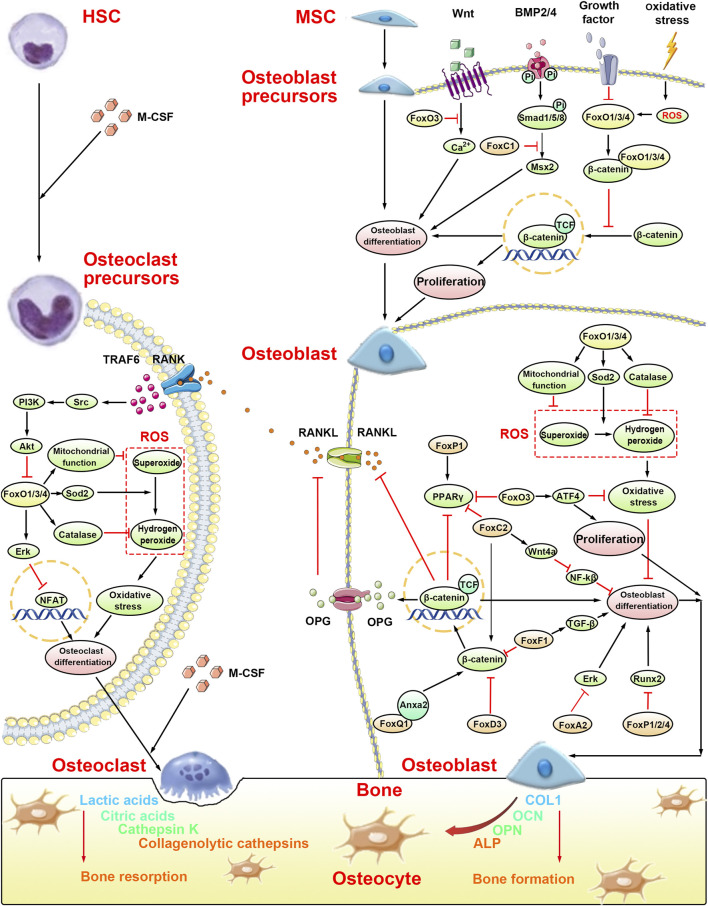
FIGURE 2.
Molecular mechanisms of bone formation and bone resorption in osteoporosis by the Fox family. The occurence of osteoporosis is caused by the imbalance of bone formation, which is caused by osteoblasts, and bone resorption, which is caused by osteoclasts. Osteoblast precursors, originated from MSC, will be suppressed in osteoblast differentiation by FoxC1 and FoxO1/3/4. Meanwhile, FoxO1/3/4 can suppress the proliferation of osteoblast precursors by binding with β-catenin. In osteoblast, FoxA2, FoxC2, FoxD3, and FoxP1/2/4 suppress osteoblast differentiation. However, FoxO1/3/4 and FoxQ1 promote osteoblast differentiation. Interestingly, FoxF1 not only suppress osteoblast differentiation by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway but also promote osteoblast differentiation by the TGF-β signaling pathway. Furthermore, FoxO3 can promote proliferation of osteoblast precursors by activating ATF4. Osteoclast precursors, originated from HSC, will be suppressed in osteoclast differentiation by FoxO1/3/4 through the Erk signaling pathway and ROS-dependent pathway.