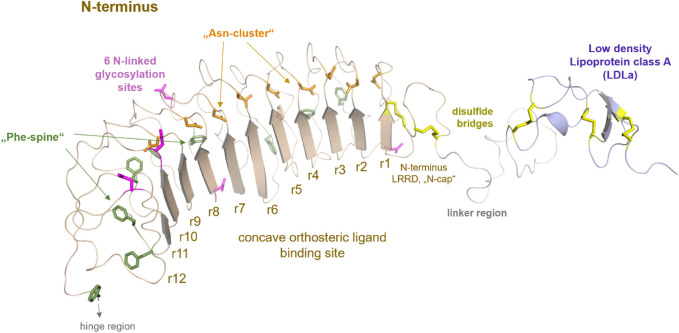
FIGURE 2.
Putative structural details of extracellular RXFP1 modules. The extracellular RXFP1 N-terminus consists of four modules according to structural templates of homologous receptors and sequence properties: (i) The LDLa domain involved in signaling regulation (also complexed with a calcium ion (Hopkins et al., 2007)). (ii) The linker region between the LDLa and the LRRD. (iii) The LRRD with 12 repeating elements is each constituted by approximately 20−25 amino acids. The LRRD fold is stabilized by: 1. Two N-terminal cysteine bridges (N-cap); 2. A “Phe-spine” constituted by phenylalanines in the backbone of almost every repeat; 3. By an asparagine-enriched cluster (named Asn-cluster”) after the β-strand of each repeat, finally forming the concave β-sheet ligand binding site (Büllesbach and Schwabe, 2005). In the extracellular part, six potential glycosylation sites (Yan et al., 2008) are allocated (magenta sticks). (iv) The hinge region is short (∼30 amino acids) compared to other LGRs, such as glycoprotein hormone receptors (GPHR (Kleinau and Krause, 2009)), and contains one disulfide bridge.