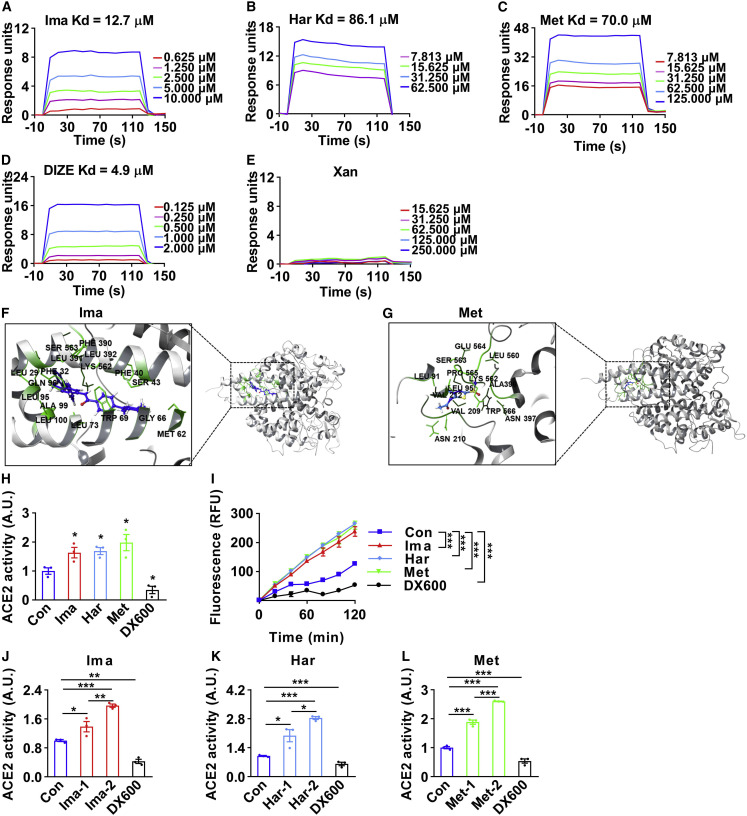
Figure 4.
Imatinib, harpagoside, and methazolamide directly bind to and activate ACE2
(A–E) The direct binding was illustrated by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assay of purified ACE2 protein with imatinib (Ima) (A), harpagoside (Har) (B), methazolamide (Met) (C), diminazene aceturate (DIZE) (D), or xanthone (Xan) (E). Xanthone was used as a negative control. The Kd values (equilibrium dissociation constant) of compounds binding to ACE2 protein were calculated based on the fitted curves.
(F and G) The detailed binding between ACE2 protein (gray) and imatinib (F, blue) and methazolamide (G, blue) was simulated with molecular dynamics simulation by GROMACS. Residues involved in binding were marked in green.
(H) The HUVECs were treated with 25 μM imatinib, 100 μM harpagoside, 100 μM methazolamide, or 1 μM DX600 for 16 h, then subjected to ACE2 enzymatic activity assay. Data shown as the area under the kinetic activity curves. The ACE2 enzymatic inhibitor DX600 was used as a negative control (n = 3).
(I–L) The HUVEC lysates were prepared and treated with 1.5 × 10−6 M imatinib, 1.5 × 10−6 M harpagoside, 1.5 × 10−6 M methazolamide, or 1.0 × 10−6 M DX600 for 30 min, then subjected to ACE2 enzymatic activity assay in a kinetics model. The kinetic activity curves were shown (I) (n = 3). The effects of imatinib (J) at concentrations of 1.5 × 10−7 M (Ima-1) and 1.5 × 10−6 M (Ima-2), harpagoside (K) at concentrations of 0.5 × 10−7 M (Har-1) and 1.5 × 10−6 M (Har-2), or methazolamide (L) at concentrations of 1.5 × 10−7 M (Met-1) and 1.5 × 10−6 M (Met-2) on the enzymatic activity of ACE2 in HUVEC lysates were shown as the area under the kinetic activity curves (n = 3).
Error bars represent SEM, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S4.