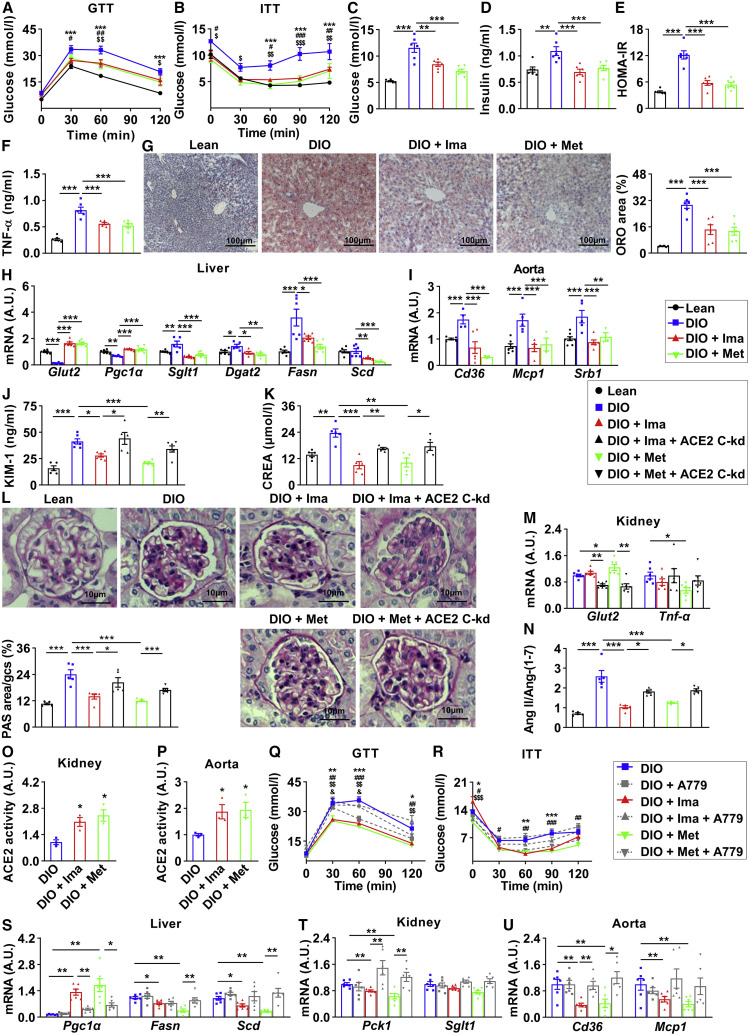
Figure 5.
Imatinib and methazolamide ameliorate metabolic defects in insulin-resistant mice via ACE2
(A–I) Twenty-eight-week-old male mice with 23-week high-fat-diet treatment (DIO) and controlled lean mice (Lean) were treated with vehicle, 250 mg/kg imatinib (DIO + Ima), or 100 mg/kg methazolamide (DIO + Met) through gavage once each day for 4 weeks.
(A and B) Glucose tolerance testing (GTT) was performed at 30 weeks (A); insulin tolerance testing (ITT) was performed at 31 weeks (B) (n = 6). The significance of lean versus DIO was shown as ∗, DIO versus DIO + Ima as #, and DIO versus DIO + Met as $. ∗,#,$p < 0.05, ∗∗,##,$$p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗,###,$$$p < 0.001. At 32 weeks, all mice were fasted for 6 h and sacrificed.
(C–F) Fasting blood glucose (C), plasma insulin (D), homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (E), and plasma TNF-α (F) (n = 6).
(G and H) Livers were subjected to oil red O (ORO) staining (G, images shown on the left, quantification on the right) and real-time PCR (H) (n = 6).
(I) Aortas were subjected to real-time PCR (n = 6).
(J–P) For kidney conditional knockdown of ACE2 (ACE2 C-kd), 26-week-old male mice with 21-week high-fat-diet treatment (DIO) and controlled lean mice (Lean) were treated with transparenchymal renal pelvis injection of AAV9-CAG-mACE2shRNA-EGFP or control virus. After 2-week recovery, mice were given vehicle, 250 mg/kg imatinib (DIO + Ima and DIO + Ima + ACE2 C-kd), or 100 mg/kg methazolamide (DIO + Met and DIO + Met + ACE2 C-kd) through gavage once each day for 4 weeks. At 32 weeks, all mice were fasted for 6 h and sacrificed.
(J and K) Plasma KIM-1 (J) and CREA (K) (n = 6).
(L and M) Kidneys were subjected to periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining (L, images and quantification were shown; n = 5) and real-time PCR (M) (n = 6).
(N) Quantification of plasma ratio of Ang II against Ang-(1–7) (n = 5).
(O and P) The lysates of kidneys (O) and aortas (P) were subjected to ACE2 enzymatic activity assay, and data were shown as the area under the kinetic activity curves (n = 3).
(Q–U) For A779 (MasR inhibitor) intervention, 28-week-old male mice with 23-week high-fat-diet treatment were given vehicle (DIO and DIO + A779), 250 mg/kg imatinib (DIO + Ima and DIO + Ima + A779), or 100 mg/kg methazolamide (DIO + Met and DIO + Met + A779) with or without 3 mg/kg A779 once each day for 4 weeks.
(Q and R) Glucose tolerance testing (GTT) was performed at 30 weeks (Q), and insulin tolerance testing (ITT) was performed at 31 weeks (R) (n = 6). The significance of DIO versus DIO + Ima was shown as ∗, DIO versus DIO + Met as #, DIO + Ima versus DIO + Ima + A779 as $ and DIO + Met versus DIO + Met + A779 as &. ∗,#,$,&p < 0.05, ∗∗,##,$$,&&p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗,###,$$$,&&&p < 0.001. At 32 weeks, all mice were fasted for 6 h and sacrificed.
(S–U) Livers (S), kidneys (T), and aortas (U) were subjected to real-time PCR.
Error bars represent SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. CREA, creatinine. See also Figure S5.